 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Using the DISJOINT operand to define disjoint subarea networks z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|
|
The DISJOINT operand on the CDRM definition statement in the cross-domain resource manager major node can also be used to control session request searches. At an interchange node, DISJOINT indicates whether an adjacent CDRM is disjoint from other SSCPs with the same NETID as the adjacent CDRM, and the only connection between the disjoint SSCPs is through the APPN network. For example, in Figure 1, HOSTA and HOSTB both have the same network identifier (NETA), but their only connection to each other is through adjacent network NETB. When a session request is received by HOSTC from HOSTA, HOSTC might decide to search the attached APPN network. When the search is forwarded into the APPN network, HOSTC includes information about the adjacent SSCP from which the request was received; namely, the HOSTA network identifier (NETA) and an indication of whether HOSTA is disjoint from other SSCPs within NETA (as defined by HOSTC using the DISJOINT operand in the CDRM definition statement for HOSTA). Figure 1. Disjoint hosts
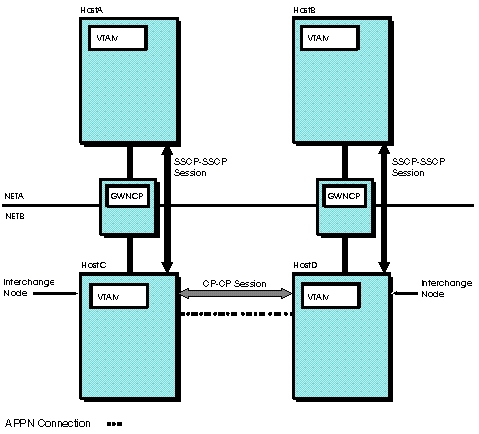 When the APPN search request is received by HOSTD, HOSTD uses this information to determine the SSCPs to which the request should be routed. HOSTD routes the request to other SSCPs that are not in NETA (the network identifier provided by HOSTC, the interchange node serving as the APPN entry point). However, when deciding whether to route the request to SSCPs within
NETA (the network identifier provided by HOSTC), HOSTD uses the DISJOINT
network indicator provided by HOSTC to make the decision. If DISJOINT=YES
was coded in HOSTC (and provided to HOSTD on the APPN search request),
HOSTD routes the search request to other SSCPs within NETA, because
it is assumed that the APPN network can provide the only connectivity
between the two disjoint parts of network NETA. If DISJOINT=NO was
coded (or allowed to default) in HOSTC, HOSTD does not route the request
to other SSCPs within NETA, because it is assumed that other connectivity
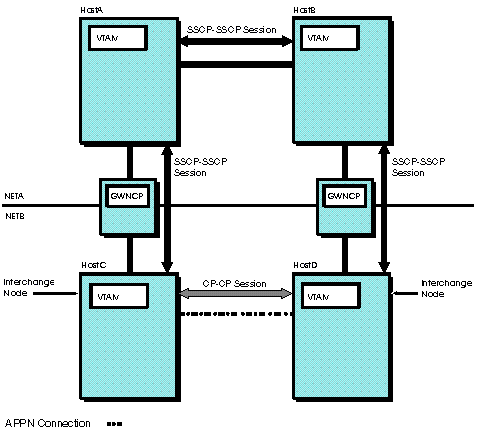
exists between HOSTA and HOSTB (see Figure 2).
When HOSTD and HOSTC fail to locate the target LU, HOSTA continues
to try other SSCPs and find the direct path to HOSTB.
Figure 2. Hosts with subarea connection


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |