z/OS CIM security
concept
Although the CIM server on z/OS is based on the open
source implementation, the security design has been considerably extended
and adapted to meet the z/OS security strengths.
The CIM server security consists of two major areas: Protection
of resources on the managed system through authentication and authorization, and protection of communicated
information through network security.
The AT-TLS feature of z/OS is used to encrypt data using SSL
for data security on the network. It is recommended to utilize this
support.
To protect resources on the managed system from unauthorized
access, first of all users have to be authenticated to ensure the CIM server is
really communicating with an identified entity (user). Users can be
authenticated by either a user identity (ID) and a password, a user
identity and a PassTicket, or a user certificate. In all cases after
successful authentication the user who wants to access the system
is well known and now authorization checks are performed against that
specific user identity.
The CIM server performs three types of authorization checks:
- For each user, the CIM server checks the authority
to access CIM. To get general access to CIM, a user needs at least READ access
to profile CIMSERV in System Authorization Facility (SAF) class WBEM.
- The access to the provider is checked. Access to a provider
can be explicitly restricted by defining a provider-specific profile
in SAF class WBEM and registering the provider with that security
profile. This access restriction is optional and depends on whether
a provider was registered with a security profile or not.
- The last checks of authorization are performed based
on the z/OS system resources a user tries to access, what effectively
means that users can only access the resources for which they were
entitled before.
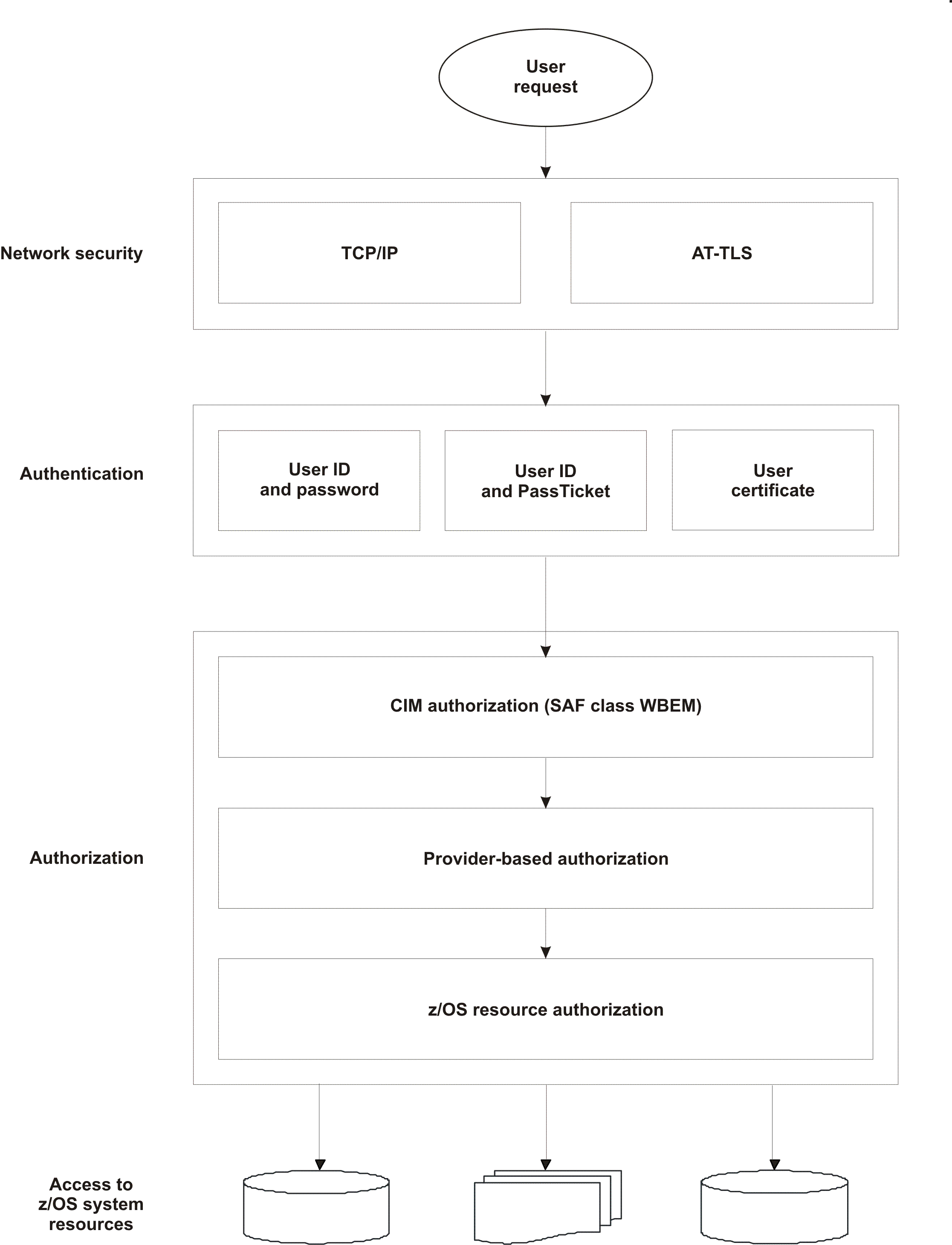
Figure 4. Security components
Figure 4 shows the CIM server runtime environment security:
- Network security
- AT-TLS provides network security. It is recommended to utilize
this feature.
- Authentication
- Authentication is always enabled for the CIM server.
The CIM server checks whether the requestor is entitled to use the
CIM server. A requestor authenticates with a user ID and a password,
with a user ID and a PassTicket, or with a user certificate.
- Authorization
-
- CIM authorization (RACF® class
WBEM)
- The CIM server controls whether the user ID is authorized to
access the CIM server using the RACF class
WBEM. The profile CIMSERV restricts access to the CIM server.
- Provider based authorization
- Optionally, a provider can be registered with a
specific security profile. In this case, the user ID has to be authorized
before it can invoke the provider. A provider-specific profile in RACF class WBEM restricts the access
to the provider.
These checks are strongly recommended for providers
which use a designated user ID.
- z/OS® resource
authorization
- The z/OS system resource access authorization is verified against
the requesting user ID.
For authorization purposes
to specific z/OS system resources, the CIM server processes requests
either under the user ID which has generated the request or under
a designated user ID which was registered for the provider. To do
this, the CIM server uses thread-level security, which is provided
by the UNIX System Services.
For that reason certain providers require additional
authorization to extra security profiles.
Additionally, the CIM server is enabled
for the Enhanced Security model. Under the
Enhanced Security model, the CIM server does not load any dynamic load
library that is not program controlled, in particular it does not
load any such provider dynamic load library.
|
 z/OS Common Information Model User's Guide
z/OS Common Information Model User's Guide
 z/OS Common Information Model User's Guide
z/OS Common Information Model User's Guide


 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014
Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014