 no
no
 yes
yes
 no
no
 yes
yes
The value of a name depends on its type, which is determined by how that name is declared. The following table shows whether a name is an lvalue expression.
| Name declared as | Evaluates to | Is an lvalue? |
|---|---|---|
| Variable of arithmetic, pointer, enumeration, structure, or union type | An object of that type | yes |
| Enumeration constant | The associated integer value | no |
| Array | That array. In contexts subject to conversions, a pointer to the first object in the array, except where the name is used as the argument to the sizeof operator. |
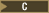 no no
|
| Function | That function. In contexts subject to conversions, a pointer to that function, except where the name is used as the argument to the sizeof operator, or as the function in a function call expression. |
|
As an expression, a name may not refer to a label, typedef name, structure member, union member, structure tag, union tag, or enumeration tag. Names used for these purposes reside in a namespace that is separate from that of names used in expressions. However, some of these names may be referred to within expressions by means of special constructs: for example, the dot or arrow operators may be used to refer to structure and union members; typedef names may be used in casts or as an argument to the sizeof operator.