The complete flow of processing, linking, and viewing the integration of internal customer data and external social media data is illustrated in this graphic. After you review the flow, use the Connecting social media data with MDM customer data tutorial for a hands-on walk-through of the entire flow.
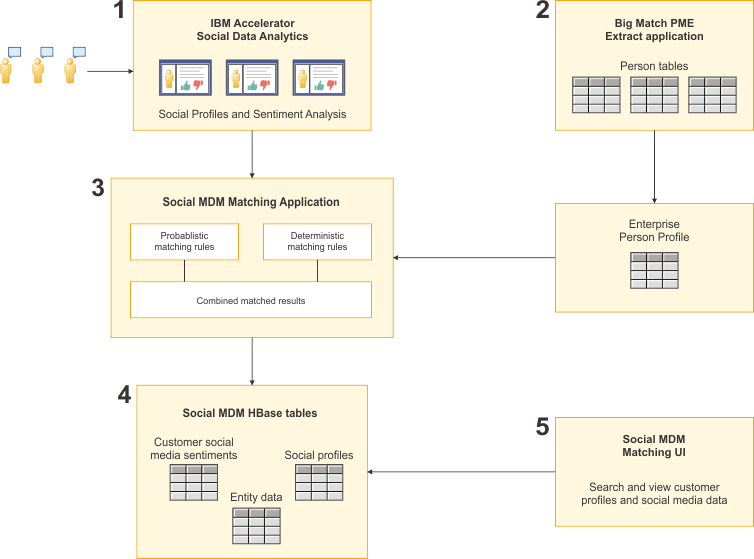
- Social media data is processed by IBM® Accelerator
for Social Data Analytics. The Social Data Analytics process outputs
two files:
- Social user profiles is a comma-separated .json file where every record represents a user profile. This file contains aggregated customer profiles.
- User sentiments file is a .csv file where each row represents a sentiment record. The sentiment file contains the actual social media comments.
Note: The Social MDM Matching sample provides a .json file that contains sample raw social media sentiments that can be used in Social Data Analytics to create the .csv file. - Customer profiles are extracted from Big Match by using the PME Extract application. Output of this step is stored as enterprise customer profiles in the Big Match extract table.
- The output of steps 1 and 2 are formatted into a sequence format
and fed into the Social MDM Matching application. The application
then uses probabilistic and deterministic matching rules (in the form
of high-level integration language (HIL) flows) to match the social
media sentiments and profiles with the enterprise customer profiles
into a single set of linkages. Note: The application uses the high-level integration language models and rules to drive entity extraction and resolution. Combining ETL-like features (such as data mapping and fusion) with entity linking and resolution rules, the language is designed for non-traditional data sources, such as partial or unknown schemas, nested or missing data, data that is extracted from text, or data that does not use traditional identifiers. The language uses entity models and rules to make connections among data facts and to match existing entities with non-traditional, unstructured data. Simply, the language enables the creation of entity-centric 360-degree data views that combine internal customer profiles with external social media data. Within the Social MDM Matching application, high-level integration language flows are run as Jaql scripts.
- The combined matching results from step 3 are placed into HBase
tables that represent the combined sentiments and enterprise customer
profiles.
- Customer social media sentiments – contains individual sentiments. The key is composed of the social profile ID, source type, and timestamp.
- Entity data - contains customer profiles. This is the same information as what is stored in the extract table, and uses the entity ID as part of the key.
- Social profiles – contains linked social profiles. The key is composed of entity ID, social profile ID, and source type.
- Finally, the Social MDM Matching user interface accesses the social HBase tables to search (Big Match Search interface sample) and view (Big Data Social Dashboard) profiles and any associated social media sentiments.

