Service Invoke mediation primitive
Use the Service Invoke mediation primitive to call a service from inside a mediation flow, as an alternative to using the callout mechanism at the end of the mediation flow.
Introduction
When you use the Service Invoke mediation primitive inside a mediation flow, the input message is used to call the service. If the call is successful, the response, or a section of the response identified by one or more XPath expressions, is used to create the output message. If the call is unsuccessful, you can retry the same service, or call another service.
You can have multiple Service Invoke mediation primitives inside one mediation flow. Therefore, you can have a series of service calls. You can use the Service Invoke mediation primitive in a request or response mediation flow.
Generally, the initial service that the Service Invoke mediation primitive calls is defined by the reference operation, which is a combination of the Reference name property and the Operation name property. For a Service Invoke mediation primitive in a subflow, the reference is defined on the subflow and resolved to a reference in the parent flow when an instance of the subflow is created.
The Service Invoke mediation primitive has one input terminal (in) and multiple output terminals. There is a fail terminal (fail) for unmodeled faults, and one output terminal for each modeled fault. Modeled faults are those that are explicitly listed in a WSDL file; any other fault is an unmodeled fault. In addition, there is an output terminal (out), which is used for successful service calls, and a timeout terminal (timeout), which is used for some types of asynchronous calls. Output terminals that are created for a specific reason are classified as dynamic terminals. For example, a WSDL-defined fault causes a dynamic output terminal to be created.
- To use the default mode, ensure that the Message Enrichment mode check box is clear.
- To enable the Message Enrichment mode, select the Message Enrichment mode check box.
Details (default mode)
In default mode, the input message, which is received at the in terminal, is passed directly to the service, and the response message from the service invocation is passed directly to the out terminal. The body and header sections of the response message are propagated to the output message.
- The message type of the in terminal must match the request message type of the reference operation.
- If there is a response message, the message type of the out terminal must match the response message type of the reference operation.
The following figure shows the message flow in default mode, for a two-way operation.
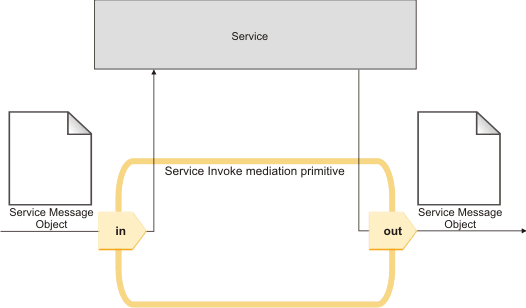
The following table summarizes the operation of the terminals of the mediation primitive in default mode.
| Terminal type | Terminal name | Dynamic terminal? | Message type | Terminal description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | in | No | WSDL message type for the request message of the operation. | Receives the input message. The message
(SMO) received at the input terminal is used to call the service. Service calls are defined by the operations specified in the WSDL. For example, you might have an operation called getCustomerDetails that calls a customer information service. |
| Output | out | Yes. WebSphere® Integration Developer defines one for the response message on the interface. | WSDL message type for the response message of the operation. | Propagates the updated message. The result
of the service call is used to make a new message (SMO) that is sent
to this terminal. Used when the service call is successful. This terminal does not exist if the operation is one-way. |
| Output | Defaults to modeled fault name. | Yes. WebSphere Integration Developer defines one for each modeled fault on the interface. | WSDL message type for the fault message of the operation. | Propagates the fault response message. No information is put in the failInfo element. Used when the relevant modeled fault is returned from the service call. |
| Output | timeout | No | WSDL message type for the request message of the operation. (Same as input terminal.) | Propagates the original message together
with the timeout exception information. The timeout exception information
is stored in the failInfo element. Used when an asynchronous
service call fails because of a timeout. The timeout terminal
is not used for calls that are asynchronous with callback, only for
calls that are asynchronous with a deferred response. This terminal does not exist if the operation is one-way. |
| Fail | fail | No | WSDL message type for the request message of the operation. (Same as input terminal.) | Propagates the original message together with any exception information. The exception information is stored in the failInfo element. Used when an unmodeled fault is returned from the service call. |
Details (Message Enrichment mode)
In Message Enrichment mode, a section of the input message, which is received at the in terminal of the Service Invoke mediation primitive, is used for the service invocation. The output message that passes through the out terminal is constructed by merging the response from the service with the original request message that was passed into the mediation primitive.
The message type of the in and out terminals must match, but the type is initially not set. When the in terminal is wired, its message type is defined implicitly by the input message, and this message type is propagated to the out terminals.
The following figure shows how the message is enriched as it flows through the mediation primitive in a two-way operation.
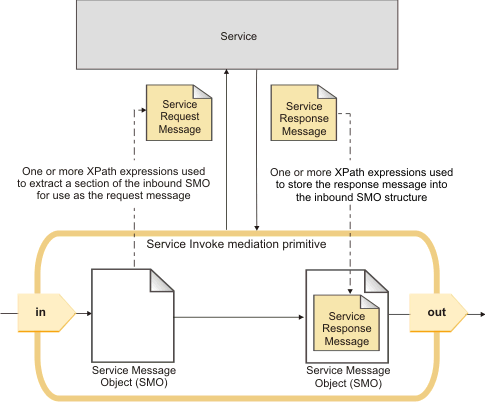
The following table summarizes the operation of the terminals of the mediation primitive in Message Enrichment mode.
| Terminal type | Terminal name | Dynamic terminal? | Message type | Terminal description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | in | No | Undefined until wire propagation causes the message type to be defined. | Receives the input message. One or more XPath expressions are used to extract a section of the inbound SMO for use as the request message. |
| Output | out | Yes. WebSphere Integration Developer defines one for the response message on the interface. | Undefined until wire propagation causes the message type to be defined. | Populates the output message by merging
the response from the service with the original request message that
was passed into the mediation primitive. This terminal does not exist if the operation is one-way. |
| Output | Defaults to modeled fault name. | Yes. WebSphere Integration Developer defines one for each modeled fault on the interface. | Undefined until wire propagation causes the message type to be defined. | Populates the fault message by merging the response from the service with the original request message that was passed into the mediation primitive. No information is put in the failInfo element. Used when the relevant modeled fault is returned from the service call. |
| Output | timeout | No | Undefined until wire propagation causes the message type to be defined. | Propagates the original message together
with the timeout exception information. The timeout exception information
is stored in the failInfo element. Used when an asynchronous
service call fails because of a timeout. The timeout terminal
is not used for calls that are asynchronous with callback, only for
calls that are asynchronous with a deferred response. This terminal does not exist if the operation is one-way. |
| Fail | fail | No | Undefined until wire propagation causes the message type to be defined. | Propagates the original message together with any exception information. The exception information is stored in the failInfo element. Used when an unmodeled fault is returned from the service call. |
Usage
- Re-send the initial request to the initial service.
- Send the initial request to an alternate service.
- Send a new request to the initial service.
- Send a new request to an alternate service.
