Create more than one broker, on one or more computers, to support your applications; creating more than one broker can provide load balancing, or a division of responsibilities. For example, you might have one broker that handles all your financial applications, and another that handles your order processing and fulfillment.
Application programs connect to and send messages to the broker, and receive messages from the broker. Code your applications to use one of the supported protocols for interacting with the broker; for example, WebSphere® MQ queues and connections, Web services, or WebSphere Adapters. The broker routes each message by using the rules that you have defined in message flows and message model schema files, and transforms the data into the structure required by the receiving application.
You can install the Integration Bus component on one or more of the supported platforms, which are listed in Operating system requirements. You can create a broker only on the computer on which you have installed the Integration Bus component. You can use the IBM Integration Explorer, the IBM Integration Toolkit, or the command line to create local brokers.
When you create a broker, it operates in one of a number of modes: advanced, adapter, standard, scale, or express. You must run the broker in the mode that matches the license that you have purchased; see Operation modes.
Administer the broker by using the IBM Integration Explorer, the Integration Nodes view in the IBM Integration Toolkit, or the product commands. Alternatively, you can write your own programs to use the IBM Integration API (also known as the CMP).
Manage the application resources of the broker, which include message flows and message model schema files, by using the IBM Integration Toolkit or IBM Integration Explorer; these two applications connect to the broker by using a WebSphere MQ server connection, which is defined to the broker queue manager when you create the broker.
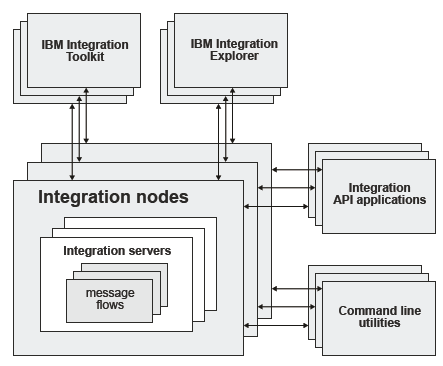
Resources associated with a broker
- A WebSphere MQ queue manager, if one does not exist.
- A set of fixed-name queues that are defined to the WebSphere MQ queue manager.
- A default WebSphere MQ SVRCONN channel with a fixed name SYSTEM.BKR.CONFIG, which is used by the IBM Integration Toolkit, the IBM Integration Explorer, and applications that use the IBM Integration API (CMP).
 Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017
Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017