A thin server instance topology or thin server instance environment consists of one non-root DB2® server instance and one or more thin DB2 server instances. In this topology, a non-root installation of DB2 database server product is performed only on the code server, rather than on each of the DB2 servers in the network. Only a minimal amount of code and configuration is required on each of the DB2 servers that deploy a thin server instance topology.
You can create a thin server instance either locally on a code server or on a remote server.
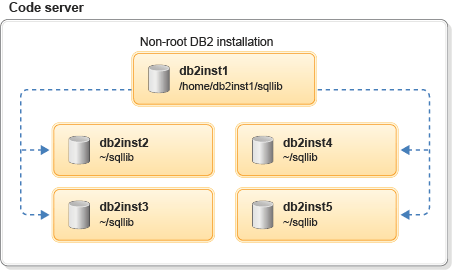
In the first case, perform a non-root installation of DB2 database server product on a code server and share the DB2 installation path as a read-only copy to other non-root users in the network through Network File System (NFS). Multiple non-root users from the same system (code server) can access the read-only copy of the shared DB2 installation path and create a thin server instance locally on the code server.
For example, if a DB2 database server is installed on System A (code server) by a non-root user db2inst1 and if that installation path is shared through NFS, then another non-root user db2inst2, can use the thin server instance environment to create an instance from the shared location of System A.
In the second case, perform a non-root installation of DB2 database server product on a code server and share the DB2 installation path as a read-only copy to other non-root users in the network through NFS (Network File System). Multiple non-root users from the remote servers that mount the read-only copy of the shared DB2 installation path on the code server can create a thin server instance locally on the remote servers.
For example, if a DB2 database server is installed on System A (code server) by a non-root user db2inst1 and if that installation path is shared through NFS and mounted on System B (remote server), then another non-root user db2inst3 can use the thin server environment to create an instance from the shared location of System A.
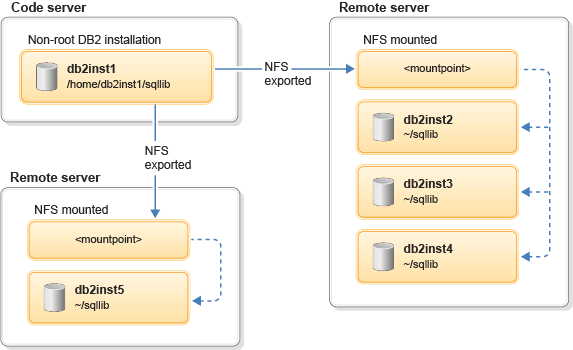
The instances that are created for db2inst2 and db2inst3 have links to the DB2 binary files on the shared location of System A. The DB2 configuration-related files are available as local files on System B.
Thin server instance environment is supported only on Linux AMD 64 bit and AIX® 64-bit operating systems. It is not supported on Sun SPARC 64 bit, HP IPF 64 bit, Sun Solaris AMD 64 bit, Linux on System z® for S/390® 64 bit, and Linux PPC 64-bit operating systems.
Thin server instance does not support database partition and pureScale® features.
Deploying a thin server instance gives you the advantage of reducing the disk space requirements on multiple systems in the network. You can create, update, drop, list, and upgrade non-root instances on multiple systems by performing a non-root installation only on one system (code server). If you use thin server instance environment for managing instances on remote servers, both the code server where the DB2 database server is installed and the remote server that mounts the shared DB2 installation path, must have the same operating system. For example, if the operating system of the code server is aix64, then the operating system of the remote server must also be aix64.
If you use thin server instance on remote server, ensure that both the code server and the remote server have the same date and time settings to ensure proper registration and evaluation of licenses on the remote server. If the date on the remote server is different from the date on the code server, then the license evaluation period expires on the remote server.
In a thin server instance environment, DB2 programs must be loaded from a code server by using a LAN connection. The extent of performance loss at program initialization time depends on variables such as the load on speed of both the network and the code server.
The following table shows the instance commands that are supported for managing non-root instances in a thin server instance environment.
| Systems | Supported | Not Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Code server |
|
Note: These commands are not supported for an instance that is
automatically created on the code server during non-root DB2 installation:
|
| Remote server |
|
|