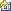In this example, Operator 1 can be a person or a recognition engine. If you use a recognition engine for the initial data entry, it runs as a background process so there is no user interface shown.
| User Interface | AltText [0] | AltText [1] | AltText [2] | Task settings in set.xml file | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator 1 (initial data entry) |
1 | 1 | Show other alt texts is
set to -1. (hide alt text) Blind confirm index is set to -1. (do not compare) |
|||
Propagate ToAltText ("1") ClearAlt Text("0") |
1 (Moved from AltText [0] |
|||||
| Operator 2 (initial state) |
1 | Show other alt texts is
set to -1. (hide alt text) Blind confirm index is set to 1. (compare) |
||||
| Operator 2 (after data entry) |
2 | 2 | 1 | Show other alt texts is
set to -1. (hide alt text) Blind confirm index is set to 1. (compare) |
||