The following diagram shows how AT-TLS works. The numbers in the
diagram represent the steps that follow the diagram.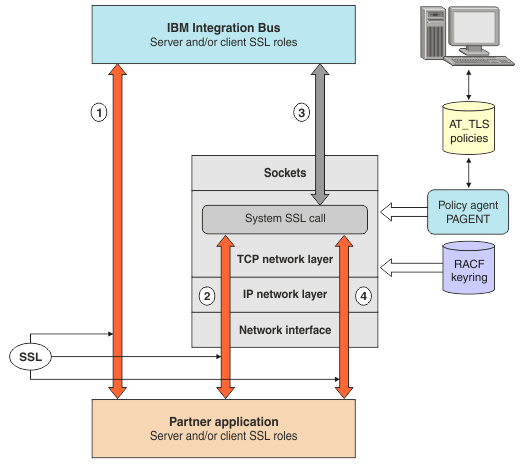

- Step 1 represents an SSL connection when AT-TLS is not used, which requires that IBM® Integration Bus and the partner application are both enabled for SSL.
- The SSL handshake is managed by AT-TLS in the TCP layer.
- Inbound or outbound application data is received or sent in the clear by IBM Integration Bus. The TCP layer validates and decrypts inbound data from partner applications, or encrypts outbound data to partner applications.
- Inbound or outbound application data is protected by SSL.
AT-TLS components
- RACF® key ring
- The RACF key ring contains the IBM Integration Bus personal certificate and the partner application signer certificate.
- AT-TLS policies
- This file contains the rules and policies that control the SSL connections that are managed by AT-TLS. These policies are created by the network administrator, and are checked and enforced by the TCP network layer of the TCP/IP stack.
- Policy Agent
- This component manages and distributes network policies, including AT-TLS policies, to the TCP/IP stack or stacks. The policy agent is also called PAGENT. For AT-TLS to function successfully, PAGENT must be configured correctly and operational.
- TCP/IP stack
- The TCP/IP stack is the component that implements the AT-TLS services. The TCP network layer is where SSL connections are intercepted, the SSL handshake is performed, and data is decrypted and encrypted. The TCP/IP stack uses RACF services to validate and accept certificates that are presented by the partner application during the handshake. RACF retrieves the IBM Integration Bus personal certificate from the key ring.
 Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017
Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017