 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Setting initial pacing values z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The type of session-level pacing and pacing window sizes are determined by the BIND request when a session is established. When an extended BIND is used, adaptive session-level pacing is requested. If adaptive-session pacing is not supported or required by the session partner, the BIND response will be sent indicating fixed-session pacing. (XBSI is the extended BIND indicator in the session initiation request. XBSI=ON means that extended BIND is used to establish the session.) The actual values used are those in the BIND response. The pacing values are carried in the BIND request flowing from the primary LU to the boundary function (if one exists for this session), and then to the secondary LU. In this way, all the participants in the session are informed of the pacing values to be used. With this in mind, the possible pacing windows for a session
are:
The direction of the data being sent determines which
pacing window values are used.
The values for the four pacing windows are derived from:
Note: An application program acting as a primary end of
a session can obtain information about pacing counts using the INQUIRE
macro instruction or the LOGON exit routine. For more information,
see z/OS Communications Server: SNA Programming.
The sources used to determine pacing-window values are
dependent on the configuration and the secondary LU (SLU). Figure 1 and Figure 2 describe the environment, and Table 1 identifies the sources used in determining the initial pacing window
value when the primary LU (PLU) is an application program. For example,
if the SLU is an application program, the pacing sources, regardless
of whether an extended BIND is sent, are described in Table 1 under:
Notes:
Figure 1. Pacing windows
for SNA LUs. Coding is from the perspective of the owning
SSCP acting as the PLU.
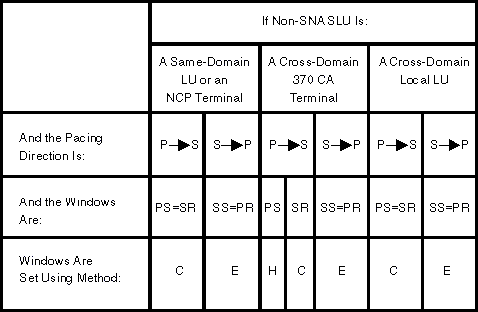
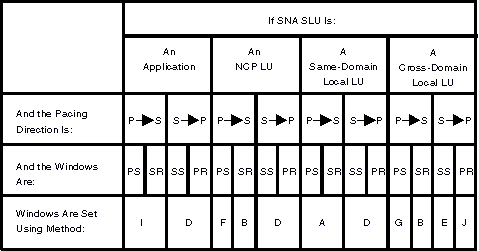 Figure 2. Pacing windows
for non-SNA LUs. Coding is from the perspective of the
owning SSCP acting as the PLU.


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |