 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Selecting session parameters for the logon mode table z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
When a logical unit requests a session with an application program, it uses a symbolic logon mode name, either directly or by default, to suggest the session protocols. Session protocols are a set of rules that describe how the session is conducted. For example, one protocol might specify the application program uses chaining for SNA requests. Another might require the logical unit does not send end-bracket indicators to the application program. For a complete description of the session protocols available in VTAM®, see z/OS Communications Server: SNA Programming. Session protocols are expressed as a string of characters called session parameters, usually specified in the logon mode table. A set of session parameters for a session is also called its logon mode. VTAM contains an IBM-supplied logon mode table, ISTINCLM. This table contains a set of generally accepted session parameters for a basic list of IBM® device types, but it might not completely meet your needs. You can create supplementary logon mode tables and associate them with device type logical units or application programs using the MODETAB operands on the definition statements defining them. To create the logon mode table:
Logon mode names are always resolved using the logon mode table associated with the secondary logical unit (SLU). For more information about which node performs the mode resolution, see Resolving logon mode names to subarea and APPN Classes of Service. Logon mode tables are created or modified using MODETAB, MODEENT, and MODEEND macro instructions. The z/OS Communications Server: SNA Resource Definition Reference describes the contents of the IBM-supplied logon mode table. It also describes how TSO can query for the logon mode being used by a terminal in place of supplying the LOGMODE during the logon. Figure 1 shows the sequence in which MODETAB, MODEENT, and MODEEND macros are coded to define a logon mode table. Figure 1. Macroinstructions for logon mode table
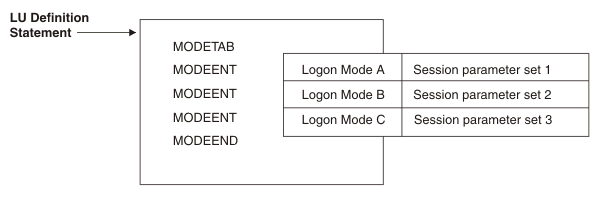 The various ways of specifying session parameters are illustrated in Table 1.
Regardless of the source of the logon or what session parameters are associated with the logon, the application program decides which session parameters are used for the session. It can decide to use the session parameters associated with the pending logon, or it can choose a different set of parameters. When the application program issues a macro to initiate a session with a logical unit, the application program indicates the logon mode name or session parameters to be used during the session. The logon mode table from which the session parameters are selected is always the one associated with the SLU, or, if a table is not associated with the logical unit, it is the IBM-supplied default logon mode table in the VTAM that owns the SLU. If the specified logon mode entry does not exist in the logon mode table associated with the secondary logical unit, the default logon mode (ISTCOSDF) is used if it is found in the table and its use is allowed as determined by the ISTCOSDF start option. You can modify or replace the IBM-supplied logon mode table, provided that the modified or replacement table has the same name as the IBM-supplied table and that the IBM-supplied table is deleted. However, because the IBM-supplied table might be needed for problem determination, you should create supplementary tables instead of deleting the IBM-supplied table. As part of the session-establishment procedures, an application
program acting as the PLU can:
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Programming describes in more detail how the application program handles session parameters. Figure 2 shows a summary of the algorithm VTAM uses to obtain session parameters. Figure 2. How session parameters are obtained from
a logon mode table
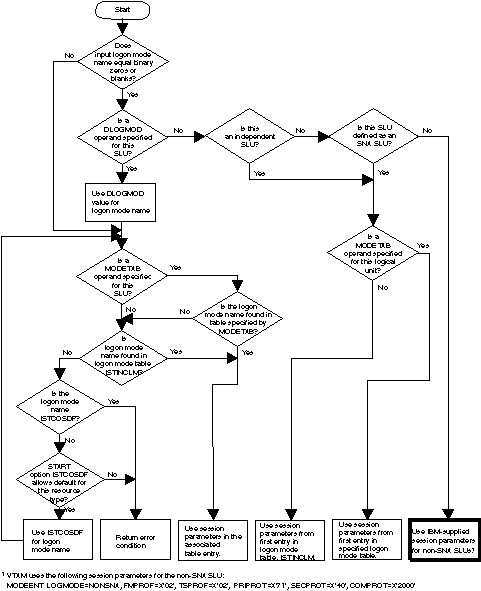 


|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |