 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Multiple connections between a type 2.1 node and a subarea node z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|
|
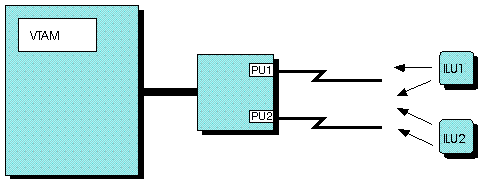
An independent LU can connect to the subarea network through only a type 2.1 PU. A type 2.1 PU can be connected to the subarea network through a type 4 or type 5 PU. The type 2.1 PU connections are called adjacent link stations. An independent LU can connect to multiple adjacent link stations. Thus, the independent LU can have multiple, simultaneous connections to the VTAM® host. If one connection fails, only the sessions using that connection must be reestablished; the other sessions are not affected. The independent LU can then use an alternative adjacent link station for any subsequent sessions. You can restart any sessions terminated by the first adjacent link-station failure and connect the independent LU through another adjacent link station. Some of the independent LU session paths might involve type 2.1 nodes connected to a VTAM other than the VTAM of the required session partner. For these sessions, the intermediate VTAM views the independent LU as a CDRSC. The CDRSC that represents the independent LU can also have other concurrent sessions that use PU type 2.1 nodes connected to the VTAM of the required session partner. If an independent LU is connected to VTAM by only LEN links and two application programs try to contact it, VTAM provides the first available adjacent link station specified on the ALSLIST operand for both application programs. Both application programs would then have parallel sessions through the same adjacent link station. If you want the application programs to use different adjacent link stations, use the adjacent link station selection function of the session management exit routine. For information about coding this exit routine, see z/OS Communications Server: SNA Customization. Figure 1 shows how an independent LU
can connect to VTAM with multiple
connections.
Figure 1. Independent
LU with multiple connections to VTAM
 Following are sample definition statements to define the configuration
in Figure 1. Note that you can support independent
LU as either destination logical units, originating LUs, or both:



|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |