 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Multiple HPR routes between HPR session endpoints z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|
|
In Figure 1, like Figure 1, none of the hosts have NCPs and all have APPN capability. In this configuration, an LU-LU session between HOSTA and HOSTD can use an RTP connection that traverses the APPN host-to-host channel connections between HOSTA and HOSTB and between HOSTB and HOSTD. For sessions between HOSTA and HOSTD, HOSTB provides only ANR-level support. However, for sessions between HOSTB and HOSTA or HOSTB and HOSTD, HOSTB can provide RTP-level support as the endpoint of an HPR route. Figure 1. Multiple HPR routes between HPR session
endpoints
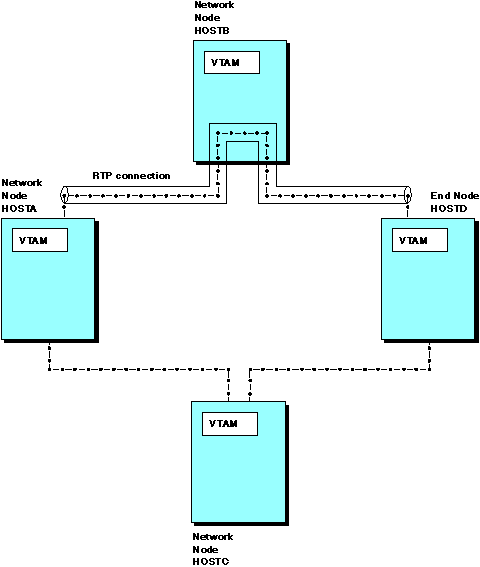 Also in Figure 1, note that an alternate HPR route exists between HOSTA and HOSTD through HOSTC. When multiple paths exist between HPR session endpoints, HPR support provides for automatic, nondisruptive path switching when a node or link fails on the path in use. For example, if the APPN host-to-host channel connection between HOSTA and HOSTB fails, HPR support provides for the movement of the RTP connection to the alternate path between HOSTA and HOSTD through HOSTC. LU-LU sessions continue uninterrupted. 


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |