 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Establishing cryptographic sessions z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cryptographic LU-LU sessions are established based on the requirements and capabilities of the session partners. As shown in Figure 1, the application
programs can establish the following sessions with the peripheral
node LUs:
Figure 1. Encryption facility specifications
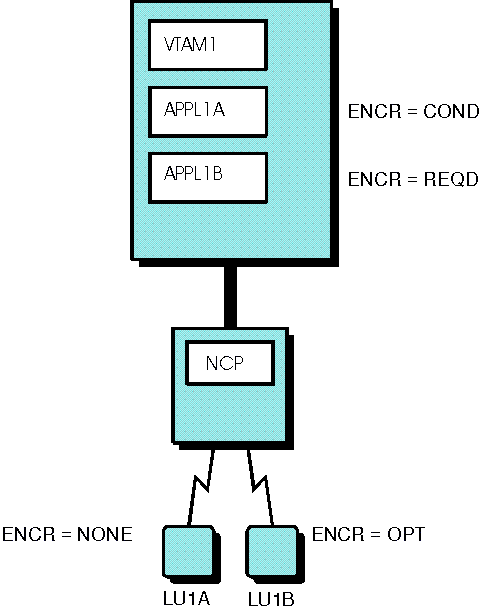 The MODIFY ENCR or MODIFY SECURITY can be used to change the cryptographic capability of a logical unit, or change the capability to a higher level of cryptography than was previously specified. Only MODIFY SECURITY can be used to change the minimum encryption type (ENCRTYPE). When VTAM® tracing is in effect for a cryptographic session, the protected data in the VTAM buffers is neither displayed nor printed. When sessions require encryption, a session could fail if a cryptographic
support is not currently available. You can define some sessions to
establish a clear session if cryptographic services are not available
at session start. The ENCR=COND operand on the APPL definition statement
specifies whether to establish a clear session if a cryptographic
facility is not available. A clear session is established when a cryptographic
facility is not available and one of the following conditions exist:
Information needed to encipher and decipher session information is included in session establishment commands. When a session that will use cryptography is being initiated, the cryptographic facility of the SLU SSCP/CP enciphers the cryptography key. From the cryptography key two enciphered keys are created:
See Cryptographic keys for a description of a cross key and how these keys are entered into the various cryptographic products. Note: The actual session data that is enciphered under the session
key is enciphered and deciphered only at the session endpoints.



|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |