 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
 z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
EE reliability and strategy z/OS Communications Server: SNA Network Implementation Guide SC27-3672-01 |
|
|
Because EE relies on IP network strategy and integrity, effective IP network design is essential to ensure successful EE implementation. The robustness of EE depends on the stability of your IP network configuration, just as any mission-critical TCP application does. With a stable IP network configuration in place, EE ensures the availability of SNA applications. In planning your EE environment, discuss your configuration with the WAN environment architect to determine whether VPN or your firewall will be affected. You should also communicate with those responsible for MVS™, because EE can affect the way OSA, OSAE, or CIP are defined. Base a well-designed IP Infrastructure on the following considerations:
Figure 1 shows the differences between a SNA network and EE using an IP network. Figure 1. Comparison between an EE network and a SNA
network
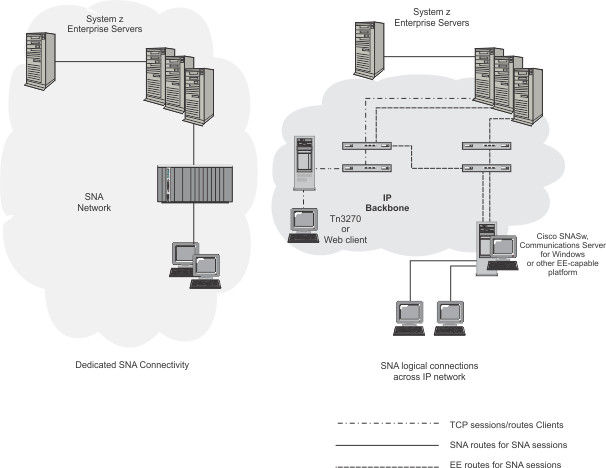 


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |