The system logger configuration you use depends on whether or not
you use a coupling facility.
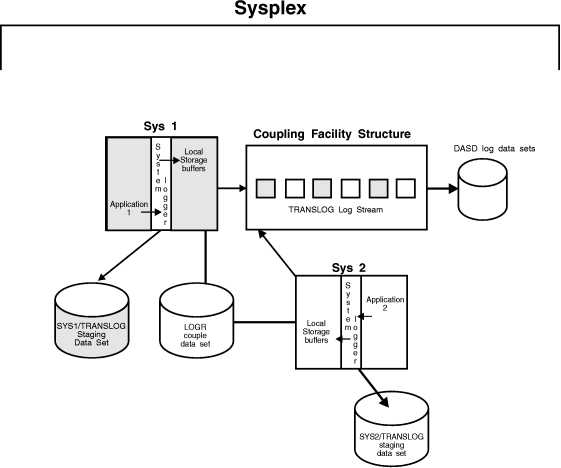
Coupling facility log stream configuration: Figure 1 shows all the parts involved when a system
logger application writes to a coupling facility log stream. In this
example, a system logger application runs on two systems in a sysplex.
Both instances of the application write data to the same log stream,
TRANSLOG. Each system contains a system logger address space. A system
logger application uses system logger services to access the system
logger capabilities.
When a system logger application writes data to a coupling facility
log stream, system logger writes the data to a coupling facility list
structure associated with the log stream. Then, when the coupling
facility structure fills with data, system logger offloads the data
to DASD log data sets.
You can optionally elect to have coupling facility data duplexed
to DASD staging data sets for a coupling facility log stream.
Figure 1. A Complete Coupling Facility Log Stream
Configuration
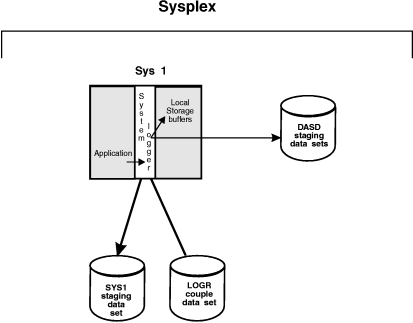
DASD-only log stream configuration:
Figure 2 shows
all the parts involved when a system logger application writes to
a DASD-only log stream. System logger writes the data to the local
storage buffers on the system, duplexing it at the same time to the
DASD staging data sets associated with the log stream. Then, when
the staging data set fills with data, system logger offloads the data
to DASD log data sets. Note that where duplexing to DASD staging data
sets is an option for a coupling facility log stream, it is a required
automatic part of a DASD-only log stream. A system logger application
uses system logger services to access the system logger capabilities.
Figure 2. A DASD-Only Configuration
For general configuration information, see the following references: