 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Track Index z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets SC23-6855-00 |
|
|
The track index is the lowest level of index and is always present. There is one track index for each cylinder in the prime area; it is written on the first tracks of the cylinder that it indexes. The index consists of a series of paired entries, that is, a normal entry and an overflow entry for each prime track. Figure 1 shows the format of a track index. Figure 1. Format of Track Index Entries
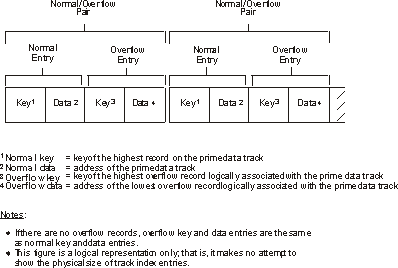 For fixed-length records, each normal entry points to record 0 or to the first data record on a track shared by index and data records. (DCBFIRSH also points to it.) For variable-length records, the normal entry contains the key of the highest record on the track and the address of the last record. The overflow entry is originally the same as the normal entry. (This is why 100 appears twice on the track index for cylinder 1 in Figure 1.) The overflow entry is changed when records are added to the data set. Then the overflow entry contains the key of the highest overflow record and the address of the lowest overflow record logically associated with the track. If all the tracks allocated for the prime data area are not used, the index entries for the unused tracks are flagged as inactive. The last entry of each track index is a dummy entry indicating the end of the index. When fixed-length record format has been specified, the remainder of the last track of each cylinder used for a track index contains prime data records, if there is room for them. Each index entry has the same format as the others. It is an unblocked, fixed-length record consisting of a count, a key, and a data area. The length of the key corresponds to the length of the key area in the record to which it points. The data area is always 10 bytes long. It contains the full address of the track or record to which the index points, the level of the index, and the entry type. 


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |