 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Alternate Index Structure for a Key-Sequenced Data Set z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets SC23-6855-00 |
|
|
Figure 1 shows the structure of an alternate index with nonunique keys connected to a key-sequenced data set. The person’s name is the alternate key in this example. The customer number is the primary key. Figure 1. Alternate Index Structure for a Key-Sequenced Data Set
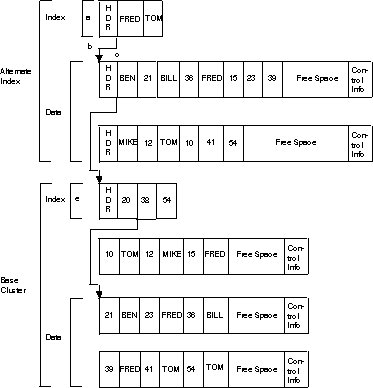 If you ask to access records with the alternate key of BEN, VSAM does the following:
RBAs are always written as fullword binary integers. 


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |