 z/OS Security Server RACF Diagnosis Guide
z/OS Security Server RACF Diagnosis Guide
 z/OS Security Server RACF Diagnosis Guide
z/OS Security Server RACF Diagnosis Guide
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Error recovery for RACF Remote Sharing Facility (RRSF) z/OS Security Server RACF Diagnosis Guide GA32-0886-00 |
|
|
This topic describes:
RRSF moves the RACF command between the user who initiated the command and the RACF subsystem address space where the transaction is processed (either on a local or a remote node) and moves the RACF command output between the RACF subsystem address space where the transaction was processed (on a local or a remote node) and the node where the user was logged on when the transaction was initiated. The INMSG data set is used to temporarily hold requests that are
being sent to the local node from itself or a remote node, such as
commands directed to the local node or output from RACF commands that were directed to a remote
node. The OUTMSG data set is used to temporarily hold requests that
are being sent to a target node, such as commands directed from the
local node. If RRSF experiences
a failure, it:
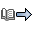
Figure 1 shows an illustration of the
flow of a directed command in an RRSF environment. The steps shown
in this figure are:
Figure 1. Flow of a Directed Command in
an RRSF Environment
 

|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |