- Automatic data
- Data that does not persist across calls. In the absence of a specific initializer, automatic data get "accidental" values that may depend on the behavior of the caller or the last function to be called by the caller.
- External data
- Data with one or more named points by which the data can be referenced by other program units and data areas. External data is known throughout an enclave.
- Local data
- Data known only to the routine in which it is declared; equivalent to local data in C, C++, or Fortran, any non-EXTERNAL data items in COBOL, and data with the PL/I INTERNAL attribute (whether implicitly, or by explicit declaration).
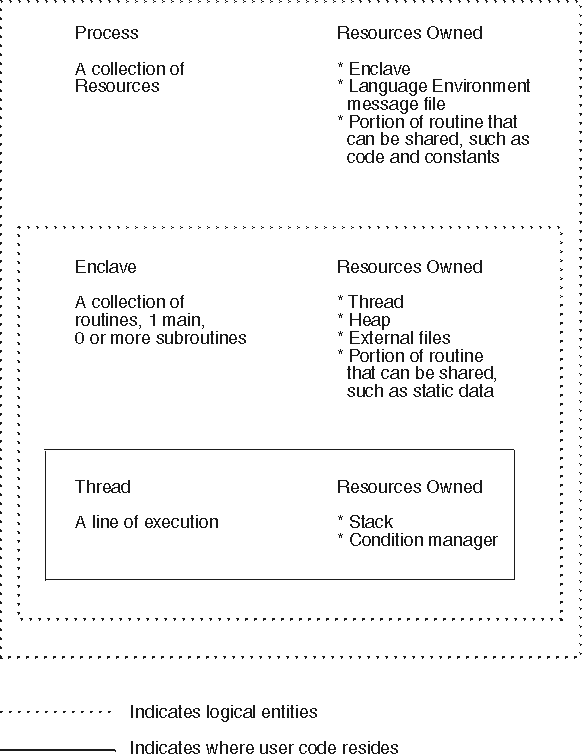
Figure 1 shows the simplest form of the Language Environment program management model and the resources that each component controls. Refer to the figure as you read about the program management model.
Figure 1. Program management
model illustration of resource ownership