About the JSON compatibility
You can combine relational and JSON data into a single query by using the JSON compatibility features.
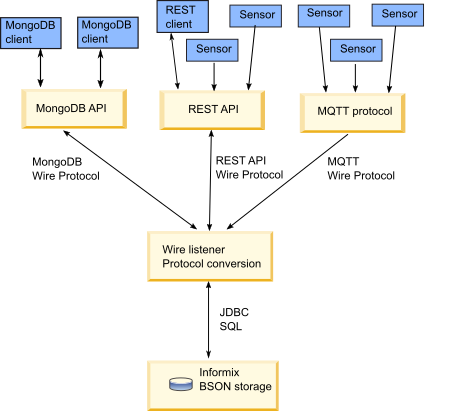
Applications that use the JSON-oriented query language can interact with relational and non-relational data that is stored in databases by using the wire listener. The database server also provides built-in JSON and BSON (binary JSON) data types.
You have the following options for accessing relational tables, including time series tables and tables with WebSphere® MQ data, and JSON collections:
- SQL API
- You can insert, update, and query data relational tables through the SQL language and standard ODBC, JDBC, .NET, OData, and other clients.
- You can access JSON collections through direct SQL access and the JDBC driver. You can use the SQL BSON processing functions to convert JSON collections to relational data types for use with ODBC, .NET, OData, and other clients.
- MongoDB API
- You can insert, update, and query data in relational tables and JSON collections through MongoDB APIs for Java™, JavaScript, C++, C#, Python, and other clients.
- REST API
- You can insert, update, and query data relational tables and JSON collections through the driverless REST API. You can run command documents that include MongoDB API commands or SQL queries. You can use the REST API to load time series data from sensor devices.
- MQTT protocol
- You can insert JSON data into relational tables and JSON collections through the MQTT protocol for Java, JavaScript, C++, PHP, Python, Ruby, and other clients. You can use the MQTT protocol to load time series data from sensor devices.
The JSON document format provides a way to transfer object information in a way that is language neutral, similar to XML. Language-neutral data transmission is a requirement for working in a web application environment, where data comes from various sources and software is written in various languages. With , you can choose which parts of your application data are better suited unstructured, non-relational storage, and which parts are better suited in a traditional relational framework.
- Define a sharded cluster to easily add or remove servers as your requirements change.
- Use shard keys to distribute subsets of data across multiple servers in a sharded cluster.
- Query the correct servers in a sharded cluster and return the consolidated results to the client application.
- Use secondary servers (similar to subordinates in MongoDB) in the sharded cluster to maximize availability and throughput. Secondary servers also have update capability.
You can choose to authenticate users through the wire listener or in the database server.
You can configure multiple wire listeners for multiple client protocols. The following illustration shows the architecture of the wire listeners and the database server.