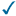
STOP CHANNEL
Use the MQSC command STOP CHANNEL to stop a channel.
| UNIX and Linux® | Windows |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Usage notes for STOP CHANNEL
- If you specify either QMNAME or CONNAME, STATUS must either be INACTIVE or not specified. Do not specify a QMNAME or CONNAME and STATUS(STOPPED). It is not possible to have a channel stopped for one partner but not for others. This sort of function can be provided by a channel security exit. For more information about channel exits, see Channel exit programs.
- On z/OS®, the command server and the channel initiator must be running.
- Any channels in STOPPED state need to be started manually; they are not started automatically. See Restarting stopped channels for information about restarting stopped channels.
- This command can be issued to a channel of any type except CLNTCONN channels (including those that have been defined automatically).
- Where there is both a locally defined channel and an auto-defined cluster-sender channel of the same name, the command applies to the locally defined channel. If there is no locally defined channel but more than one auto-defined cluster-sender channel, the command applies to the channel that was last added to the local queue manager repository.
Parameter descriptions for STOP CHANNEL
- (channel-name)
- The name of the channel to be stopped. This parameter is required for all channel types.
- CONNAME(connection-name)
- Connection name. Only channels matching the specified connection name are stopped
- MODE
- Specifies whether the current batch is allowed to finish in a controlled
manner. This parameter is optional.
- QUIESCE
- This is the default.
- FORCE
For server-connection channels, breaks the current connection, returning MQRC_CONNECTION_BROKEN.
For other channel types, terminates transmission of any current batch. This is likely to result in in-doubt situations.- TERMINATE
- On other platforms other than z/OS, this parameter terminates transmission of any current batch. This allows the command to actually
terminate the channel thread or process.
For server-connection channels, breaks the current connection, returning MQRC_CONNECTION_BROKEN.
- QMNAME(qmname)
- Queue manager name. Only channels matching the specified remote queue manager are stopped
- STATUS
- Specifies the new
state of any channels stopped by this command. For details about channels in STOPPED state, and
especially SVRCONN channels, see Restarting stopped channels.
- STOPPED
- The channel is stopped. For a sender or server channel the transmission queue is set to
GET(DISABLED) and NOTRIGGER.
This is the default if QMNAME or CONNAME are not specified.
- INACTIVE
- The channel is inactive.
This is the default if QMNAME or CONNAME are specified.
