Database topologies
You use the metadata repository to store imported metadata, project configurations, reports, and results for all components of IBM® InfoSphere® Information Server. The metadata repository is included as part of the metadata repository tier, which can include additional product module data stores as separate databases or database schemas. The metadata repository is also used to keep a registry of these data stores, to include their locations and connection information. The staging area is created along with the metadata repository.
Depending on which product modules you install, the repository tier can include the following data stores:
- one or more InfoSphere Information Analyzer analysis databases
- the InfoSphere QualityStage® Match Designer database
- the Standardization Rules Designer database
- an operations database to support the IBM InfoSphere DataStage® and QualityStage Operations Console
- IBM InfoSphere Data Quality Console Exceptions database
For most of the databases, the installation program will register
them in the metadata repository and create and configure them as necessary.
You can also choose to manually register and set them up with the
help of the RepositoryAdmin tool
as a post-installation step.
RepositoryAdmin,
and the topics that describe the use of the tool still refers to data
stores as repositories in certain contexts.- Staging area
- Stores metadata that is imported from external data sources so that it can be examined before it is moved to the active metadata repository. Managed from InfoSphere Metadata Asset Manager.
- Analysis databases
- Analysis databases store high-volume, detailed analysis results,
such as column analysis, primary key analysis, and domain analysis. InfoSphere Information Analyzer projects
can share an analysis database, or you can associate each project
with a specific analysis database.
If you install InfoSphere Information Analyzer, you must provide the location for one or more analysis databases. After the installation, you can add additional databases by using the InfoSphere Information Server console.
The analysis database might be used by a single InfoSphere Information Analyzer project, or it might be shared by multiple projects. For example, two InfoSphere Information Analyzer projects might use two different analysis databases, or they might share the same analysis database.
- Match Designer database
- The InfoSphere QualityStage Match
Designer is a component of InfoSphere QualityStage that
is used to design and test match specifications. Match specifications
consist of match passes that identify duplicate entities within one
or more files.
The InfoSphere Information Server installation program does not create the Match Designer results database. You can create the database before or after the installation, as long as the database is configured and accessible when you use the Match Designer. You can create the database on a computer where the client or engine tier is installed or on any computer that is accessible to both of these tiers. You must configure the database to receive the type of data that is processed in the Match Designer. For example, you must configure the database to receive double-byte data if the Match Designer processes Asian data.
- Standardization Rules Designer database
- The Standardization Rules Designer database
is a component of InfoSphere QualityStage that
is used to enhance standardization rule sets. After you enhance rule
sets in the Standardization Rules Designer,
you can apply the enhanced rule sets in a Standardize stage.
By default, the InfoSphere Information Server installation program creates the Standardization Rules Designer database as a separate schema in the metadata repository database.
- Exceptions database
- In InfoSphere Information Server products and components, entities that might require additional information or investigation are called exceptions. Information about each set of exceptions is provided by exception descriptors that are stored in the exceptions database. The exceptions database is managed from the IBM InfoSphere Data Quality Console.
These data stores can reside in the same database system installation as distinct databases or database schemas. Alternatively, other than the staging area, which must be located in the same database (but in a different schema) as the active metadata repository, you can locate the data stores and the metadata repository on different computers. The database system that you choose can be different from the database system for your other databases. For example, you can use an IBM DB2® database for the metadata repository and an Oracle database for the Match Designer database.
If you are creating a database system installation for a database, determine where to locate the instance and the database. The database must be accessible by the computers where the services tier and engine tiers are installed.
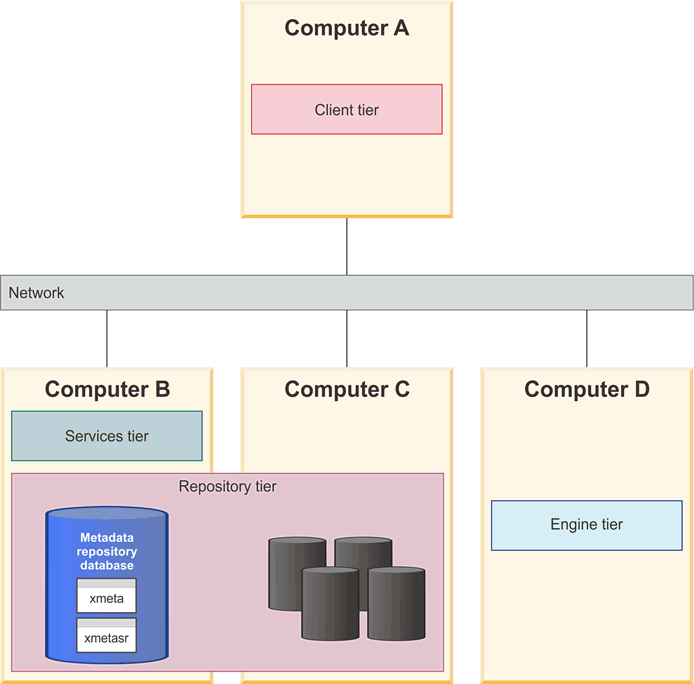
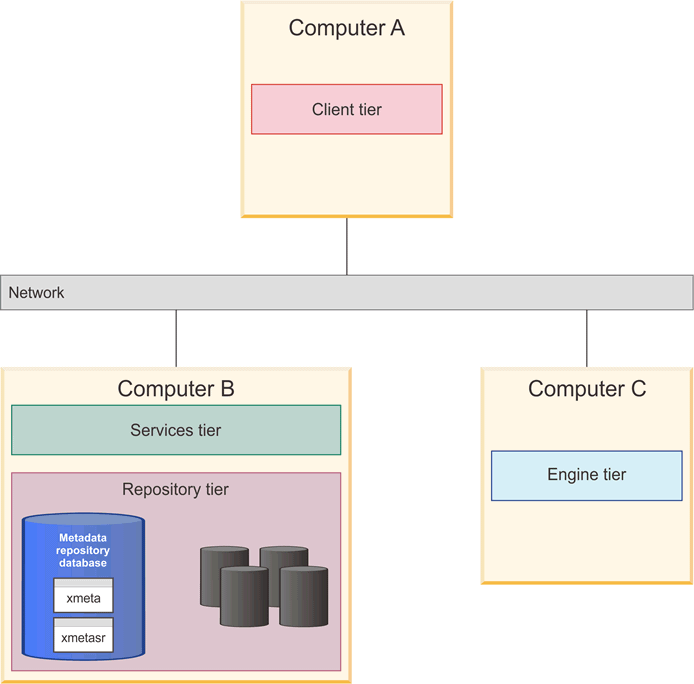
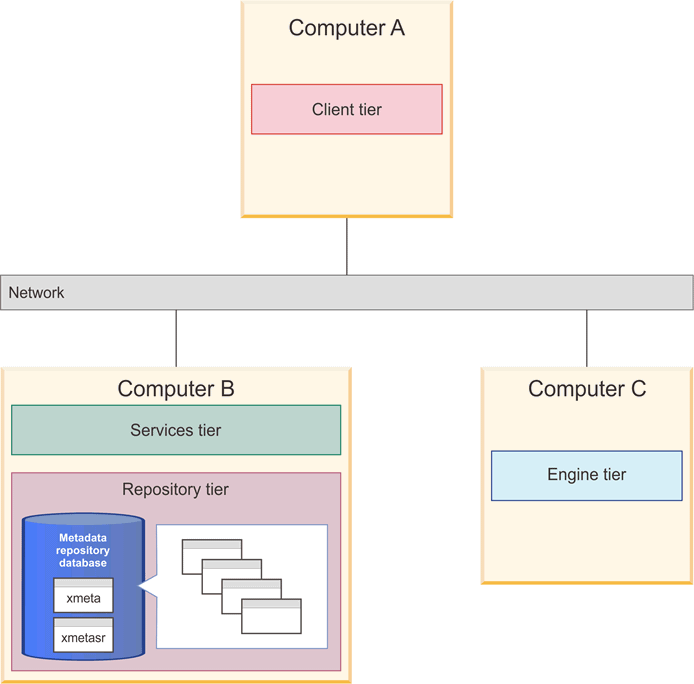
The following two diagrams illustrate a three-computer topology where the data stores are located on the same computer as the metadata repository database. They can be created in separate databases or in separate schemas in the same or different databases. Figure 2 illustrates data stores as separate schemas within the metadata repository database. This is possible for all data stores except the analysis databases, which must be in their own database.
The following diagram illustrates a four-computer topology where the analysis databases and other data stores are on a separate computer from the metadata repository database.