Planning for firewall traffic between the xscmd utility and data grid servers
You must plan for data grid traffic between the xscmd utility and data grid servers.
The examples illustrate where you must allow communication between the xscmd utility and data grid servers. You should read the port properties and values that are defined in Planning for network ports.
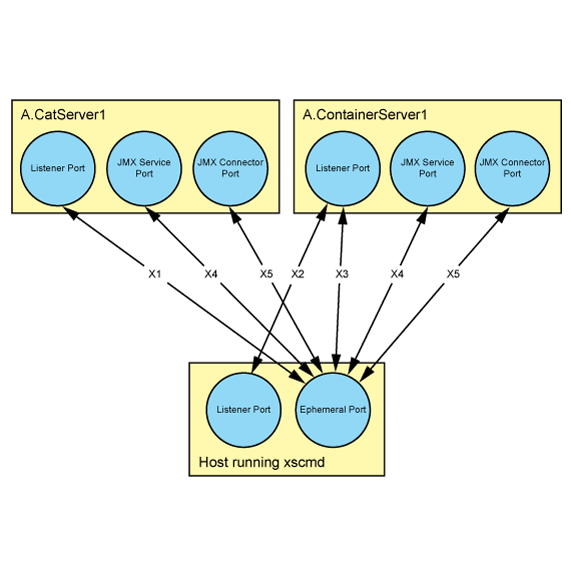
- X1: Only the host that runs the xscmd utility can initiate traffic.
- If a listener port is not configured, it will default to 2809. In this
example, the listener port is set to 2809. Outbound traffic uses source port:
ephemeral, destination port: 2809, and return traffic from the data grid
servers flows over the same connection.Note: When a data grid server operates inside WebSphere Application Server and uses an ORB transport protocol, another port ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS must also be opened. The BOOTSTRAP_ADDRESS port forwards requests to this port.
- X2: ORB transport protocol only. Both sides can initiate traffic.
- If a listener port is not configured for the client or server, an ephemeral port is chosen and
this port can vary each time the client or server is restarted. In this example, the listener port
is set to 2809. For traffic that is initiated by the host running the
xscmd command utility, outbound traffic uses source port: ephemeral, destination
port: 2809, and return traffic from container server flows over the same
connection. Similarly, for traffic that is initiated by the data grid server, outbound traffic uses
source port: ephemeral, destination port: 2809, and return traffic from the
host flows over the same connection.Note: When a data grid server operates inside WebSphere Application Server and uses an ORB transport protocol, another port ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS must also be opened. The BOOTSTRAP_ADDRESS port forwards requests to this port.
- X3: IBM® eXtremeIO (XIO) transport protocol only. Only the host that runs the xscmd utility can initiate traffic.
- If a listener port is not configured, an ephemeral port is chosen at startup and this port can vary each time that the server is restarted. In this example, the listener port is set to 2809. Outbound traffic uses source port: ephemeral, destination port: 2809, and return traffic from the data grid servers flows over the same connection.
- X4: Only the host that runs the xscmd utility can initiate traffic.
- If a Java Management Extensions (JMX) service port is not configured for a catalog server, the data grid server uses the default of 1099 for a catalog server and a dynamic port is chosen for a container server. This port can vary each time that the container server is restarted. In this example, the JMX service port is set to 1099. Outbound traffic uses source port: ephemeral, destination port: 1099, and return traffic from the data grid server flows over the same connection.
- X5: Only a host that runs xscmd utility can initiate traffic.
- In this example, a JMX connector port is set to 32701. Outbound traffic uses source port: ephemeral, destination port: 32701, and return traffic from the data grid server flows over the same connection.
Note:
- If Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is not configured, but a JMX connector port is configured, firewall traffic uses the JMX connector port.
- If SSL is not configured and a JMX connector port is not configured, firewall traffic uses the JMX service port.
- If SSL is configured, but a JMX connector port is not configured, an ephemeral port is chosen. This port can vary each time that the server is restarted. Firewall traffic flows over the ephemeral port.