Maps
A map is a container for key-value pairs, which allows an application to store a value indexed by a key. Maps support indexes that can be added to index attributes on the key or value. These indexes are automatically used by the query runtime to determine the most efficient way to run a query.
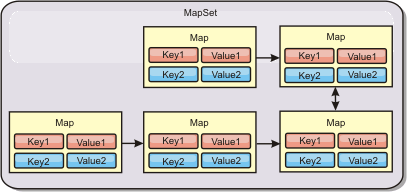
A map set is a collection of maps with a common partitioning algorithm. The data within the maps are replicated based on the policy defined on the map set. A map set is only used for distributed topologies and is not needed for local topologies.
WebSphere® eXtreme Scale can store serializable Java™ objects ![]() or eXtreme data format (XDF) serialized
objects in each of the maps using the ObjectMap API for Java clients
or eXtreme data format (XDF) serialized
objects in each of the maps using the ObjectMap API for Java clients![]()
![]() or the IGridMapAutoTx/IGridMapPessimisticTx API
for .NET clients. A schema can be defined over the maps to identify the relationship between
the objects in the maps where each map holds objects of a single type. Defining a schema for maps is
required to query the contents of the map objects. WebSphere eXtreme Scale
can have multiple map schemas defined.
or the IGridMapAutoTx/IGridMapPessimisticTx API
for .NET clients. A schema can be defined over the maps to identify the relationship between
the objects in the maps where each map holds objects of a single type. Defining a schema for maps is
required to query the contents of the map objects. WebSphere eXtreme Scale
can have multiple map schemas defined.
For more information about caching objects, see Getting started tutorial module 2: Create a client application.
WebSphere eXtreme Scale can also store entities using the EntityManager API. Each entity is associated with a map. The schema for an entity map set is automatically discovered using either an entity descriptor XML file or annotated Java classes. Each entity has a set of key attributes and set of non-key attributes. An entity can also have relationships to other entities. WebSphere eXtreme Scale supports one to one, one to many, many to one and many to many relationships. Each entity is physically mapped to a single map in the map set. Entities allow applications to easily have complex object graphs that span multiple Maps. A distributed topology can have multiple entity schemas.
For more information about caching objects with the EntityManager API, see Caching objects and their relationships (EntityManager API).