Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive
Use the Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive to route service requests within a Service Gateway. There are three different modes: URL, XPath and Action. The URL and XPath modes will be used when the module is acting as a proxy gateway and endpoint lookups are based on the virtual service name. The Action mode is used to resolve SOAP Actions or WS-Addressing Actions within WebSphere Service Registry and Repository for Dynamic and Static Service Gateway patterns.
Introduction
You can use the Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive to create various types of service gateway.
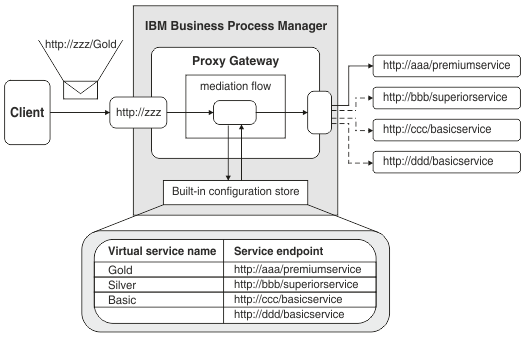
You can create a proxy gateway that routes requests to virtual services defined in proxy groups. A proxy gateway is a specific type of service gateway that defines proxy groups with which the administrator can associate real endpoints. Alternatively, you can create other types of services gateways that route to web service endpoints, based on the action specified in the message.
If you create a proxy gateway, the service definitions are stored in a built-in configuration store. If you create another type of service gateway, the service definitions are stored in WebSphere® Service Registry and Repository (WSRR).
The Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive has one input terminal (in), two output terminals (out and nomatch) and a fail terminal (fail). The in terminal is wired to accept a message and the other terminals are wired to propagate a message. If a suitable endpoint is found, the out terminal propagates a message that includes the endpoint. If an endpoint is not found, the nomatch terminal is fired. You can wire the nomatch terminal to another mediation primitive that decides where to forward the message to. If an exception occurs during the routing resolution, the fail terminal propagates the input message, together with any exception information contained in the failInfo element.
Details
- The dynamic callout address, in the SMO header, is set with the first match: /headers/SMOHeader/Target/address
- The alternate targets list, in the SMO header, is updated with the remaining matches: /headers/SMOHeader/AlternateTarget
- All services found are also placed in the primitive context: /context/primitiveContext/EndpointLookupContext
The Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive uses the Endpoint Reference structure defined by the WS-Addressing specification. For more information, see: http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/08/addressing.
URL and XPath Modes: Proxy gateways, proxy groups, and virtual services
In IBM® Integration Designer, you can use the Patterns Explorer view of the Business Integration perspective to create a proxy gateway. Use the menu options: . The Patterns Explorer creates a mediation flow that includes the Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive.
To create a proxy gateway you must define one or more proxy groups, using the Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive. When you install the proxy gateway module to IBM Business Process Manager, the proxy groups are created in a built-in configuration store.
Using the Gateway Endpoint Lookup mediation primitive, you must also specify a point in the request message where the name of a virtual service can be found. A virtual service is a proxy for one or more real services. You specify whether the virtual service name is found using the inbound URL, which is the default, or an XPath. After you have installed the proxy gateway module, you can use a Business Space widget to define the virtual services in the proxy groups. Using the Proxy Gateway widget, you create associations between the virtual services and the real service endpoints; the associations are stored in the built-in configuration store.
Before a client can access a proxy gateway, it needs the WSDL to call a virtual service. You can retrieve the WSDL by entering the endpoint of the virtual service URL in a web browser, and appending the string: ?wsdl. For example, http://zzz/Gold?wsdl, where http://zzz/ is the address of the proxy gateway and Gold is the name of the virtual service.
- Proxy Group Name: One or more proxy groups that are created in the built-in configuration store, when the module is installed. IBM Business Process Manager has a built-in configuration store.
- Lookup Method: whether the virtual service name is the same as the input URL, or found using an XPath expression.
- Lookup XPath: If you specify a Lookup Method of XPath, you must specify where the virtual service name can be found in the SMO.
Action Mode: Service gateways and action-based routing
In order for a service gateway to use action-based routing, a web service request must contain an action either in the SOAPAction field or the WS-Addressing Action field. If a web service request contains both action fields, the values of the fields must be the same.
- Lookup Method: set the Lookup Method to Action.
- Registry Name: Either the name of a particular instance of WSRR, or IBM Business Process Manager, or the default instance.
- User Properties
- Classification
Usage
Service gateways act as proxies to services and allow you to access multiple services from one address. In addition, service gateways can encapsulate transformations, routing, and common processing. Both the Gateway Endpoint Lookup primitive and the Endpoint Lookup primitive can be used to create service gateways.
If you want to route requests based on the action specified by a message, use the Gateway Endpoint Lookup primitive to create a service gateway with a lookup method of action.