The high availability feature of DAG backups improves Exchange Server data backups and data recovery. You can use Exchange Server 2010 and later features with DAG backups.
- A group of up to 16 mailbox servers can host up to 100 mailbox databases.
- Up to 16 online copies of a database (1 active database and up to 15 passive databases).
- Replication through log shipping.
- Synchronous or lagged replication.
- Automatic migration and failover of active database copies.
- Query DAG database copies, including status.
- Manage full, copy, incremental, and differential backups of active and passive databases within a DAG.
- Query all DAG database copy backups.
- Restore all DAG database copy backups.
- Restore into an active database, from either active or passive database copy backups.
- Restore into a recovery or alternate database.
- Individual Mailbox Restore (IMR) from a DAG database copy backup.
- Delete DAG database copy backups.
- When you back up to LOCAL, the restore, delete, and automatic expire operations can be completed only on the Exchange Server where the backup was taken.
- Restores must be done on an active database copy.
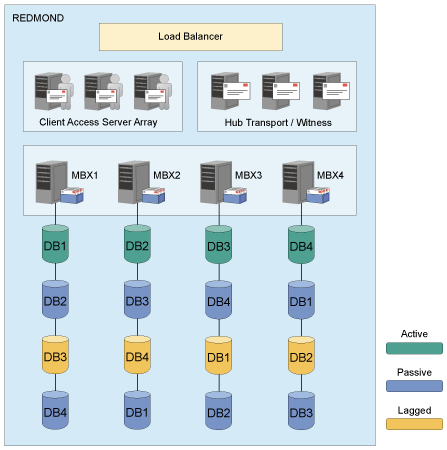
Sample DAG configuration
DAG members often hold a subset of the Exchange databases in a combination of active and passive copies to optimize use of available server resources.
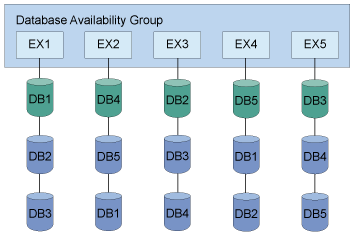
Backing up solutions
You can back up data from any DAG member and restore the data to any DAG member. You can also back up data from either the active or passive copy. Full and incremental database backups do not need to be completed from the same DAG member. All databases included in a VSS type backup are snapped together.
When backing up data, provide options from backup deployment. You want to distribute the backup workload for scalability and isolate backup activity to a dedicated backup node. Isolating backup activity minimizes the impact to production databases.
Ideally, avoid redundant backups of the same databases. Recognizing all replicas as copies of the same database helps achieve this goal. You can also apply retention policies to "unique" databases.
Allowing backups from any node in the availability group and enabling restores from any node in the availability group is also ideal.
Achieving these goals
The DAGNODE parameter provides a common namespace for all backups. Each node authenticates separately with Tivoli Storage Manager. The backup data is stored in DAGNODE namespace using the Asnode option.
To indicate that a backup is taken from a passive copy unless no healthy passive copy is available, use the PREFERDAGPASSIVE parameter.
If the Exchange Server databases belong to a DAG and are an active database copy, the EXCLUDEAGACTIVE parameter excludes the databases from the backup.
If the Exchange Server databases belong to a DAG and are a passive database copy, the EXCLUDEDAGPASSIVE parameter excludes the databases from the backup.
To specify the minimum amount of time before a backup of another DAG copy of the same database is allowed, use the MINIMUMBACKUPINTERVAL parameter.
The synchronization mechanism between the Data Protection client instances on the same DAG ensures that two nodes do not simultaneously start a backup of the same database.
Sample data protection deployments in DAG environments
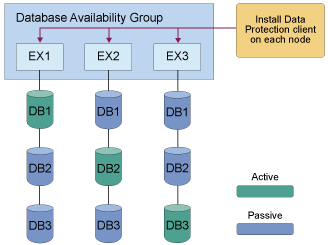
tdpexcc backup DB1 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassive
tdpexcc backup DB2 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassive
tdpexcc backup DB3 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassive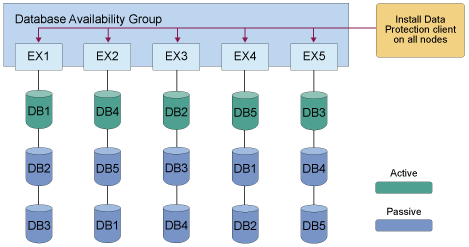
tdpexcc backup DB1 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassive
tdpexcc backup DB2 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassive
tdpexcc backup DB3 full /minimumbackupinterval=60 /preferdagpassiveAgain, note that each line is different per node.
Database Availability Group backup best practices
Complete backups for replicated database copies from the same Exchange Server. Additionally, complete backups on the passive database copies. When you backup passive database copies, you do not increase the load on the production Exchange Server.
- Perform backups from a passive database copy to avoid increasing the load on the active databases.
- Schedule all DAG members with a copy of the database to back up the database at the same time. In addition, specify the /MINIMUMBACKUPINTERVAL parameter. When you specify this parameter, only one backup is taken per backup cycle.
- Optionally, use the /EXCLUDENONDAGDBS command-line backup option to exclude the databases that are not part of the DAG.
- Use the /EXCLUDEDAGPASSIVE, /EXCLUDEDAGACTIVE, or /EXCLUDENONDAGDBS command-line backup options to exclude certain databases from backup processing. You can also use the /MINIMUMBACKUPINTERVAL and /PREFERDAGPASSIVE backup options.
- When there are two or more healthy database copies, the integrity check can be skipped by using the /SKIPINTEGRITYCHECK flag.