| Destination |
Yes |
Yes |
None |
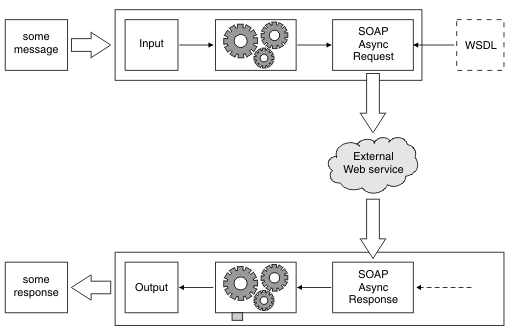
The destination to which the node sends outgoing
messages. If the SOAPAsyncRequest node is to be used to send point-to-point messages, enter the
Destination queue name for the JMS queue name that is listed in the
bindings file. This property takes its initial value from a WSDL
URI property, depending on whether the WSDL address URI is formatted in the W3C (standards) style, or the IBM (proprietary) style. Destination is set to the value
of destinationName found
in the WSDL if a W3C-style URI is found, or destination if an IBM-style URI
is found.
|
jmsDestination |
|---|
| Reply To Destination |
Yes |
Yes |
None |
The name of the JMS destination to which the
receiving application must send a reply message. For a reply message
to be returned to this JMS destination, the JMS destination name must
be known to the domain of the JMS provider that is used by the receiving
client. If the Get Response By
Correl ID property is cleared, this queue uniquely identifies
messages destined for the paired SOAPAsyncResponse node. If
the Get Response By Correl ID property is checked, this queue can then be shared between multiple
nodes.
This property takes its initial value from a WSDL URI
property, depending on whether the WSDL address URI
is formatted in the W3C (standards) style, or the IBM (proprietary) style. Reply To Destination is set to the
value of replyToName found
in the WSDL if a W3C-style URI is found, or to the first of replyToName, replyTo, replyToDestination, or replyDestination if an IBM-style
URI is found. If any of these other properties are present, they display
as a name-value pair in the User
Parameters table.
|
jmsReplyToDestination |
|---|
| JMS provider name |
Yes |
No |
WebSphere
MQ |
Select a JMS vendor name from the list, or enter
a name of your choice. The name must match the name of a configurable
service that is defined for the broker to which you deploy the message
flow. When you select a name from the list, the Initial context factory property
is updated automatically with the relevant Java™ class. If you enter your own JMS provider
name, you must also enter a value for the Initial context factory.
|
|
|---|
| Initial context factory |
Yes |
Yes |
com.sun.jndi.fscontext.
RefFSContextFactory |
The starting point for a JNDI namespace. A JMS application uses the initial context to obtain and look up
the connection factory and queue or topic objects for the JMS provider. If you select a JMS provider name from the list in JMS provider name, the Initial context factory property
is updated automatically with the relevant Java class. If you enter your own JMS provider
name, you must also enter a value for the Initial context factory. The default
value is com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory, which defines the file-based Initial
context factory for the WebSphere MQ JMS provider.
This property takes its initial value
from a WSDL URI property, depending on whether the WSDL address URI is formatted in the W3C (standards) style, or the IBM (proprietary) style. Initial context factory is set to
the value of jndiInitialContextFactory found in the WSDL if a W3C-style URI is found, or initialContextFactory if an IBM-style
URI is found.
|
initialContextFactory |
|---|
| JNDI URL bindings location |
Yes |
Yes |
|
The system path or the LDAP location for the
bindings file. The bindings file contains definitions for the JNDI
administered objects that are used by the SOAPAsyncRequest node. This
property is disabled when the Initial
context factory is com.ibm.mq.jms.Nojndi.
When you enter a value for JNDI URL bindings location, ensure
that it complies with the following instructions: - Construct the bindings file before you deploy a message flow that
contains a SOAPAsyncRequest node.
- Do not include the file name of the bindings file in this field.
- If you have specified an LDAP location that requires authentication,
configure the LDAP principal (userid) and LDAP credentials (password)
separately. These values are configured at broker level. For information
about configuring these values, see mqsicreatebroker command and mqsichangebroker command.
- The string value must include a supported URL prefix
that has a URL handler that is available on the class path.
For information about constructing the JNDI administered
objects bindings file, see the JMS provider documentation.
This
property takes its initial value from a WSDL URI property, depending
on whether the WSDL address URI is formatted in the
W3C (standards) style, or the IBM (proprietary) style. JNDI URL bindings
location is set to the value of jndiURL found in the WSDL if a W3C-style URI is found, or jndiProviderURL if an IBM-style
URI is found.
|
locationJndiBindings |
|---|
| Connection factory name |
Yes |
Yes |
|
The name of the connection factory that is used
by the SOAPAsyncRequest node to create a connection to the JMS provider. This property
is initially configured from the imported WSDL. This name must exist
in the bindings file. The Connection
factory name must be a JMS QueueConnectionFactory. This property takes its initial value from a WSDL URI property, depending
on whether the WSDL address URI is formatted in the
W3C (standards) style, or the IBM (proprietary) style. Connection
factory name is set to the value of jndiConnectionFactoryName found
in the WSDL if a W3C-style URI is found, or connectionFactory if an IBM-style
URI is found.
|
connectionFactoryName |
|---|
| User Parameters |
No |
No |
|
This table describes user properties that will
be sent in the requestURI property of the outgoing request message. The properties are name-value
pairs that exist in the WSDL and are not used by other properties
of the SOAPAsyncRequest node. |
|
|---|
| JNDI parameters |
No |
No |
|
A table mapping JNDI context parameters to their
type. These properties take their initial values from any W3C-style
WSDL properties starting with jndi-. IBM-style WSDL does not support JNDI parameters, but you can set
these properties on the node.
|
|
|---|
| Get Response By Correl ID |
No |
Yes |
Cleared |
If this property is checked, the SOAPAsyncRequest node sends
the request message with the Correl ID specified in the Unique identifier property, and
the SOAPAsyncResponse node
receives only response messages that match that Correl ID. This allows
a single Reply To Destination queue to be shared between several pairs of SOAPAsyncRequest and SOAPAsyncResponse nodes, if
this property is checked for all those nodes. This functionality
works only with web service providers that support reading the Correl
ID from the request message and using it as the Correl ID in the response
message.
|
|
|---|
| Backout destination |
No |
Yes |
|
The SOAPAsyncResponse node sends
response messages to this destination when errors prevent the response
message flow from processing the response message. The message is
removed from the reply to destination.
The backout properties
are set by the SOAPAsyncRequest node, but used only by its paired SOAPAsyncResponse node.
|
backoutDestination |
|---|
| Backout threshold |
No |
Yes |
0 |
This value controls when a message is put
to the backout destination. For example, if the value is 3, the JMS
provider attempts to deliver the message to the input destination
three times. After the third attempted delivery, the message is not
rolled back to the reply to destination and is sent to the Backout
destination.
The backout properties are set by the SOAPAsyncRequest node, but
used only by its paired SOAPAsyncResponse node.
See Configuring the backout threshold property.
|
|
|---|

 Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017
Last updated Friday, 21 July 2017