IBM Integration API
The IBM® Integration API is a remote programming interface that your custom integration applications can use to control integration nodes and their resources.
Use the IBM Integration API to interact with the integration node to perform the following tasks:
- Deploy BAR files
- Change the integration node configuration properties
- Create, modify, and delete integration servers
- Inquire and set the status of the integration node and its associated
resources, and be informed if the status of any of following items
changes:
- Integration servers
- Deployed message flows
- Deployed files that are used by the message flows (for example, JAR files)
- View the Administration log
- View the Activity log
- Create and modify message flow applicationsNote: When you use IBM Integration API, all changes to configurable properties values in BAR files that are already deployed are temporary. The properties revert to their previous values after the next deployment of any flow in the same integration server.
To view the Javadoc for the IBM Integration API, see IBM Integration API.
For the Java user-defined node API, which applies to user-defined nodes and to Java code that is called by JavaCompute nodes, see Java user-defined extensions API information.
Interaction between custom integration applications and the integration node
For applications that interact with the integration node, the Java classes sit logically between the user application and the integration node, inside the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) of the user application.
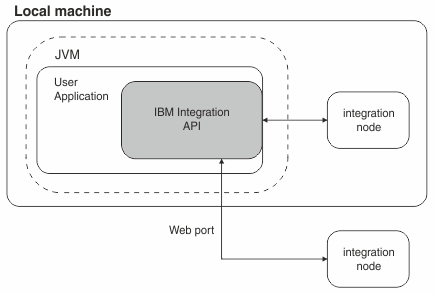
The custom integration application can be on the same physical machine as the integration node, or on a remote machine. If a connection is made to a remote machine, the connection is made through the web administration port; for more information, see Configuring the IBM Integration Bus web user interface.
Migrating from earlier versions of IBM Integration Bus
For information about migrating your custom integration applications to Version 10.0, see Migrating custom integration (CMP) applications.