q_data structure for math and bit-manipulation conditions
For conditions that occur in the mathematical or bit manipulation routines, the Language Environment condition manager creates q_data that user condition handlers can use to handle the condition. The q_data structure is shown in Figure 1, and is the same for all entry points of the mathematical and bit manipulation routines.
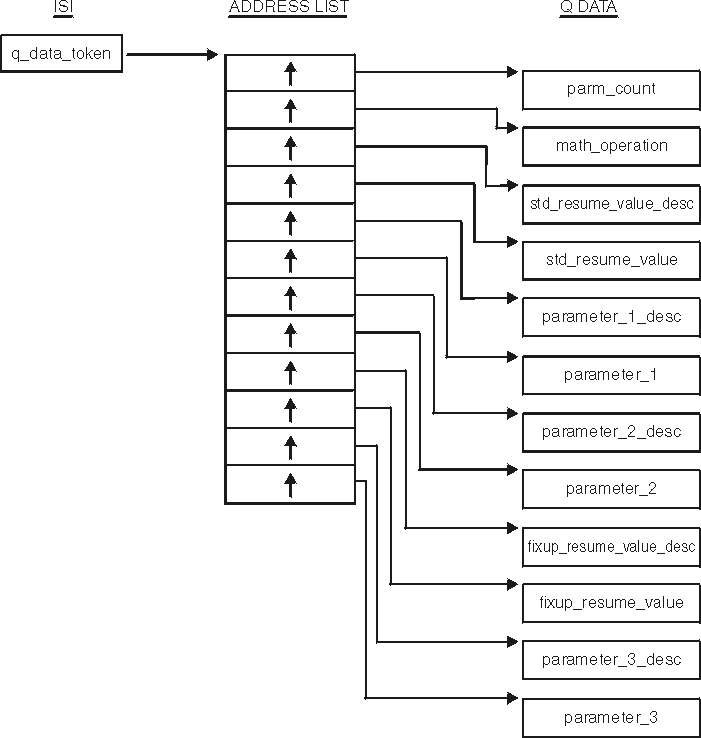
- q_data_token (input)
- The 4-byte address of the address list. This value is returned by the CEEGQDT callable service.
- parm_count (input)
- A 4-byte binary integer containing the value 10, which is the total number of q_data fields in the q_data structure, including parm_count.
- math_operation (input)
- An 8-byte field containing an abbreviation for the mathematical or bit manipulation operation for which the condition occurred. The field is left-justified and padded with blanks. (See Table 1 for a list of the abbreviations.)
- std_resume_value_desc (input)
- The q_data descriptor for std_resume_value.
- std_resume_value (input)
- A default value used as the result of the mathematical or bit manipulation function when the user condition handler requests the resume action (result code 10). The length and type of this field are dependent on math_operation and are reflected in the q_data descriptor std_resume_value_desc.
- parameter_1_desc (input)
- The q_data descriptor for parameter_1.
- parameter_1 (input/output)
- The value of the first parameter provided to the mathematical
or bit manipulation routine. The length and type of this field are
dependent on math_operation and are reflected in the q_data
descriptor parameter_1_desc.
This is the value of the first parameter that is used as input to the routine when the user condition handler requests a resume with new input value (result code 60 with a new condition token of CEE0CE).
- parameter_2_desc (input)
- The q_data descriptor for parameter_2 if the mathematical or bit manipulation routine has two input parameters. (If the routine has only one parameter, the q_data structure has an address slot for this field, but the address is not meaningful and the field must not be referenced.)
- parameter_2 (input/output)
- The value of the second parameter provided to the mathematical
or bit manipulation routine if the routine has two input parameters.
(If the routine has only one parameter, the q_data structure has an
address slot for this field, but the address is not meaningful and
the field must not be referenced.) The length and type of the field
are dependent on math_operation and are reflected in the q_data
descriptor parameter_2_desc.
This is the value of the second parameter that is used as input to the routine when the user condition handler requests a resume with new input value (result code 60 with a new condition token of CEE0CE).
- fixup_resume_value_desc (input)
- The q_data descriptor for fixup_resume_value. (See Format of q_data descriptors for more information about q_data descriptors.)
- fixup_resume_value (output)
- The value to be used as the result of the mathematical or bit manipulation function when the user condition handler requests a resume with new output value (result code 60 with a new condition token of CEE0CF). The length and type of this field are dependent on math_operation and are reflected in the q_data descriptor fixup_resume_value_desc.
- parameter_3_desc (input)
- The q_data descriptor for parameter_3 if the mathematical or bit manipulation routine has three input parameters. (If the routine has only one (or two) parameter(s), the q_data structure has an address slot for this field, but the address is not meaningful and the field must not be referenced.)
- parameter_3 (input/output)
- The value of the third parameter provided to the mathematical
or bit manipulation routine if the routine has three input parameters.
(If the routine has only one (or two) parameter(s), the q_data structure
has an address slot for this field, but the address is not meaningful
and the field must not be referenced.) The length and type of the
field are dependent on math_operation and are reflected in
the q_data descriptor parameter_3_desc.
This is the value of the third parameter that is used as input to the routine when the user condition handler requests a resume with new input value (result code 60 with a new condition token of CEE0CE).
| Mathematical operation | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Logarithm Base e | LN |
| Logarithm Base 10 | LOG |
| Logarithm Base 2 | LOG2 |
| Exponential (base e) | E**Y |
| Exponentiation (x raised to the power y) | X**Y |
| Arcsine | ARCSIN |
| Arccosine | ARCCOS |
| Arctangent | ARCTAN |
| Arctangent2 | ARCTAN2 |
| Sine | SIN |
| Cosine | COS |
| Tangent | TAN |
| Cotangent | COTAN |
| Hyperbolic Sine | SINH |
| Hyperbolic Cosine | COSH |
| Hyperbolic Tangent | TANH |
| Hyperbolic Arctangent | ARCTANH |
| Square Root | SQRT |
| Error Function | ERF |
| Error Function Complement | ERFC |
| Gamma Function | GAMMA |
| Log Gamma Function | LOGGAMMA |
| Absolute Value Function | ABS |
| Modular Arithmetic | MOD |
| Truncation | TRUNC |
| Imaginary Part of Complex | IPART |
| Conjugate of Complex | CPART |
| Nearest Whole Number | NWN |
| Nearest Integer | NINT |
| Positive Difference | POSDIFF |
| Transfer of Sign | XFERSIGN |
| Floating Complex Multiply | CPLXMULT |
| Floating Complex Divide | CPLXDIVD |
| Bit Shift | ISHFT |
| Bit Clear | IBCLR |
| Bit Set | IBSET |
| Bit Test | BTEST |