 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
 z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets
|
Previous topic |
Next topic |
Contents |
Contact z/OS |
Library |
PDF
Accessing Data Sets Using DFSMStvs and VSAM Record-Level Sharing z/OS DFSMS Using Data Sets SC23-6855-00 |
|
|
This topic describes the use of VSAM data sets for DFSMStvs. VSAM record-level sharing (RLS) is an access option for VSAM data
sets that allows transactional (such as Customer Information Control
System (CICS) and DFSMStvs), and non-transactional applications to
concurrently access data. This option provides multisystem sharing of
VSAM data sets across a z/OS Parallel Sysplex®. VSAM
RLS exploits the data sharing technology of the coupling facility
(CF) including a CF-based lock manager and a CF cache manager. VSAM
RLS uses the CF-based lock manager and the CF cache manager in its
implementation of record-level sharing.
Note: VSAM RLS requires that the data sets be System Managed Storage
(SMS) data sets. To be eligible for RLS, a data set that is not already
SMS-managed must be converted to SMS.
RLS is a mode of access to VSAM data sets. RLS is an access option interpreted at open time. Select the option by specifying a new JCL parameter (RLS) or by specifying MACRF=RLS in the ACB. The RLS MACRF option is mutually exclusive with the MACRF NSR (nonshared resources), LSR (local shared resources), and GSR (global shared resources) options. This topic uses the term non-RLS access to distinguish between RLS access and NSR, LSR, and GRS access. Access method services do not use RLS when performing an IDCAMS EXPORT, IMPORT, PRINT, or REPRO command. If the RLS keyword is specified in the DD statement of a data set to be opened by access method services, the keyword is ignored and the data set is opened and accessed in non-RLS mode. See Using Non-RLS Access to VSAM Data Sets for more information about non-RLS access. RLS access is supported for KSDS, ESDS, RRDS, and VRRDS data sets, and for VSAM alternate indexes. The VSAM RLS functions are provided by the SMSVSAM server. This server resides in a system address space. The address space is created and the server is started at MVS IPL time. VSAM internally performs cross-address space accesses and linkages between requestor address spaces and the SMSVSAM server address space. The SMSVSAM server owns two data spaces. One data space is called the SMSVSAM data space. It contains some VSAM RLS control blocks and a system-wide buffer pool. VSAM RLS uses the other data space, called MMFSTUFF, to collect activity monitoring information that is used to produce SMF records. VSAM provides the cross-address space access and linkage between the requestor address spaces and the SMSVSAM address and data spaces. See Figure 1. Figure 1. VSAM
RLS address and data spaces and requestor address spaces
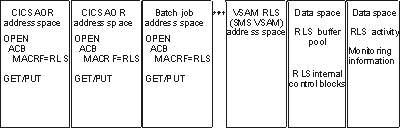 VSAM RLS data buffers occupy the largest share of the SMSVSAM data-space storage. In some cases, storage limits on the data buffers may create performance slowdowns in high-volume transaction environments. To avoid any storage limits and potentially enhance performance, VSAM RLS offers the option to move RLS data buffers into 64-bit addressable virtual storage. This option can be activated by assigning VSAM data sets to a data class with ISMF that specifies RlsAboveTheBar(YES). IBM recommends that you use this option, especially for applications with a high rate of critical CICS transactions. For details on setting up and using this option, see Using 64-Bit Addressable Data Buffers 


|
 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 Copyright IBM Corporation 1990, 2014 |