Web content authoring environments
An authoring environment is used to create and manage web content and is used by your content creators and website designers.
Server type
Most Web Content Manager sites need to support many content creators. A clustered server solution is the best solution for this scenario.Standard authoring environment
A standard authoring environment consists of a single authoring cluster that syndicates directly to either a staging or delivery environment. The authoring environment may be used to create drafts, approve drafts, test changes, publish changes, and syndicate to the delivery environment. For example:

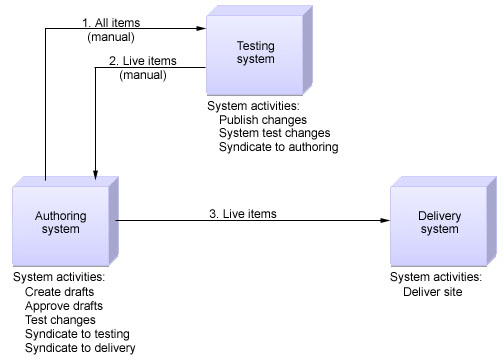
Authoring environment with testing
You can add a test environment to your authoring environment to enable you to perform user acceptance testing on your content management system and website. You can create drafts, approve changes, test changes, and syndicate to staging from the authoring environment. In the Site UAT environment, you can publish the changes, have the system test the changes, and syndicate to the authoring environment. From the authoring environment, you can syndicate to the delivery environment. For example:
Decentralized authoring environments
If you content creators are located at different locations, or you have different groups of content creators, you might consider deploying a set of decentralized authoring clusters. This scenario works best if the decentralized content creators work with separate content stored in different content libraries.For example, if you have users located in different locations, it may be more efficient to install a local authoring environment at each location. Two-way syndication is used between all authoring environments with a centralized authoring environment to allow changes made at all remote locations to be visible to all users.

Decentralized authoring creates the risk of conflicting updates between authoring environments. To reduce the risk of conflicts, you can allocate different sites, or different sections of a site, to each authoring environment. You can also use different authoring environments for different user roles. For example, Content creators could use a different authoring environment than presentation template designers.
Access to each decentralized authoring environment is controlled using a combination of authoring portlet access controls and item security settings. For example, Only users requiring access to the local authoring environment would be granted access to the local authoring portlet. Users would be given "Read" access to all items, but only "Edit" access to items they are required to update.