Two operator characteristics determine how operands group with operators: precedence and associativity. Precedence is the priority for grouping different types of operators with their operands. Associativity is the left-to-right or right-to-left order for grouping operands to operators that have the same precedence. An operator's precedence is meaningful only if other operators with higher or lower precedence are present. Expressions with higher-precedence operators are evaluated first. The grouping of operands can be forced by using parentheses.
b = 9; c = 5; a = b = c;
Because the order of subexpression evaluation is not specified, you can explicitly force the grouping of operands with operators by using parentheses.
a + b * c / dthe * and / operations are performed before + because of precedence. b is multiplied by c before it is divided by d because of associativity.
The following tables list the C and C++ language operators in order of precedence and show the direction of associativity for each operator. Operators that have the same rank have the same precedence.
| Rank | Right associative? | Operator function | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | yes | 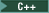 global scope resolution global scope resolution |
:: name_or_qualified name |
| 1 | 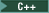 class or namespace scope resolution class or namespace scope resolution |
class_or_namespace :: member | |
| 2 | member selection | object . member | |
| 2 | member selection | pointer -> member | |
| 2 | subscripting | pointer [ expr ] | |
| 2 | function call | expr ( expr_list ) | |
| 2 | value construction | type ( expr_list ) | |
| 2 | postfix increment | lvalue ++ | |
| 2 | postfix decrement | lvalue -- | |
| 2 | yes | 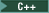 type identification type identification |
typeid ( type ) |
| 2 | yes | 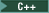 type identification at run time type identification at run time |
typeid ( expr ) |
| 2 | yes |  conversion checked at compile time conversion checked at compile time |
static_cast < type > ( expr ) |
| 2 | yes |  conversion checked at run time conversion checked at run time |
dynamic_cast < type > ( expr ) |
| 2 | yes |  unchecked conversion unchecked conversion |
reinterpret_cast < type > ( expr ) |
| 2 | yes |  const conversion const conversion |
const_cast < type > ( expr ) |
| Rank | Right associative? | Operator function | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | yes | size of object in bytes | sizeof expr |
| 3 | yes | size of type in bytes | sizeof ( type ) |
| 3 | yes | prefix increment | ++ lvalue |
| 3 | yes | prefix decrement | -- lvalue |
| 3 | yes | bitwise negation | ~ expr |
| 3 | yes | not | ! expr |
| 3 | yes | unary minus | - expr |
| 3 | yes | unary plus | + expr |
| 3 | yes | address of | & lvalue |
| 3 | yes | indirection or dereference | * expr |
| 3 | yes |  create (allocate memory) create (allocate memory) |
new type |
| 3 | yes |  create (allocate and initialize memory) create (allocate and initialize memory) |
new type ( expr_list ) type |
| 3 | yes |  create (placement) create (placement) |
new type ( expr_list ) type ( expr_list ) |
| 3 | yes |  destroy (deallocate memory) destroy (deallocate memory) |
delete pointer |
| 3 | yes |  destroy array destroy array |
delete [ ] pointer |
| 3 | yes | type conversion (cast) | ( type ) expr |
| Rank | Right associative? | Operator function | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 |  member selection member selection |
object .* ptr_to_member | |
| 4 |  member selection member selection |
object ->* ptr_to_member | |
| 5 | multiplication | expr * expr | |
| 5 | division | expr / expr | |
| 5 | modulo (remainder) | expr % expr | |
| 6 | binary addition | expr + expr | |
| 6 | binary subtraction | expr - expr | |
| 7 | bitwise shift left | expr << expr | |
| 7 | bitwise shift right | expr >> expr | |
| 8 | less than | expr < expr | |
| 8 | less than or equal to | expr <= expr | |
| 8 | greater than | expr > expr | |
| 8 | greater than or equal to | expr >= expr | |
| 9 | equal | expr == expr | |
| 9 | not equal | expr != expr | |
| 10 | bitwise AND | expr & expr | |
| 11 | bitwise exclusive OR | expr ^ expr | |
| 12 | bitwise inclusive OR | expr | expr | |
| 13 | logical AND | expr && expr | |
| 14 | logical inclusive OR | expr || expr | |
| 15 | conditional expression | expr ? expr : expr | |
| 16 | yes | simple assignment | lvalue = expr |
| 16 | yes | multiply and assign | lvalue *= expr |
| 16 | yes | divide and assign | lvalue /= expr |
| 16 | yes | modulo and assign | lvalue %= expr |
| 16 | yes | add and assign | lvalue += expr |
| 16 | yes | subtract and assign | lvalue -= expr |
| 16 | yes | shift left and assign | lvalue <<= expr |
| 16 | yes | shift right and assign | lvalue >>= expr |
| 16 | yes | bitwise AND and assign | lvalue &= expr |
| 16 | yes | bitwise exclusive OR and assign | lvalue ^= expr |
| 16 | yes | bitwise inclusive OR and assign | lvalue |= expr |
| 17 | yes |  throw expression throw expression |
throw expr |
| 18 | comma (sequencing) | expr , expr |