Moving your custom configuration to the target environment
During the
migration, many of the customizations that you made in the source
environment are automatically applied to the target environment.
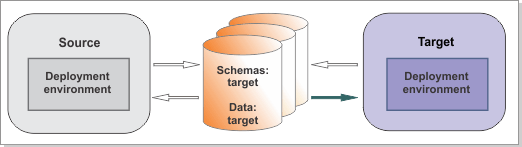
Figure 1. Sample environment after the target is
started. The source environment is not running. The target can read
from the databases.
About this task
The values that you used for your customized properties in the source environment are automatically applied to the target environment, unless you changed them when you edited the BPMConfig properties file.
Procedure
- Some WebSphere Lombardi Edition XML properties
are automatically migrated to IBM® BPM configuration
files. See WebSphere
Lombardi Edition XML configuration properties that are migrated to
WebSphere Application Server configuration files for a list
of these properties. The rest are copied from 100Custom.xml to 101CustomMigrated.xml.
If you modified the 100Custom.xml file for Process
Center (Process Server) or Performance Data Warehouse, verify that
it has been copied to the correct folder. For example:
- The 101CustomMigrated.xml file for Process Center (Process Server) is created in install_root\profiles\deployment_manager_profile\config\cells\cell_name\nodes\node_name\servers\application_cluster_name\process-center\config
- The 101CustomMigrated.xml file for Performance Data Warehouse is created in install_root\profiles\deployment_manager_profile\config\cells\cell_name\nodes\node_name\servers\support_cluster_name\performance-data-warehouse\config
- If you are migrating from
a network deployment environment, the values of the following performance
tuning parameters are migrated automatically. See the reference topic
for more information.
- J2C activation specification tuning parameters
- Data source tuning parameters
- JVM tuning parameters
- Thread pool tuning parameters
- Topic connection factory tuning parameters
- Transaction service tuning parameters
- Web container tuning parameter
- Work manager information tuning parameters
Restriction: If you are migrating from a stand-alone environment, you must migrate these values manually.- To check the J2C activation specification
tuning parameters, in the administrative console, click Resources > Resource Adapters > J2C activation specifications.
Click the activation specification and click J2C activation
specification custom properties.
Table 1. J2C activation specification tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope maxBatchSize The maximum batch size for a message-driven bean. These properties are migrated only in the application cluster and support cluster scope. Properties for the following JNDI names might be migrated, depending on the source environment: - eis/DataDefLoaderActivationSpec
- eis/EventMgrControlActivationSpec
- eis/EventMgrMessageActivationSpec
- eis/InterServerActivationSpec
- jms/PortalWebMessagingActivationSpec
- eis/PostLoadCalculationActivationSpec
- eis/RepresentationManagerActivationSpec
- eis/ViewManagerActivationSpec
- bpm/pal/service/deployActivationSpec
- eis/cacheMessageActivationSpec
- sca/WLE_de_name.app_cluster_name/ActivationSpec
maxConcurrency The maximum number of instances of a message-driven bean. - To check the data source tuning parameters,
click Resources > JDBC > Data sources. Click the data
source and click Connection pool properties.
Table 2. Data source tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Maximum connections The maximum number of physical connections to the datastore that can be created in the connection pool. When this number is reached, no new physical connections are created; requestors must wait until a physical connection that is in use is returned to the pool. These properties are migrated if they exist in your migration source. These properties are migrated for the following data source in the cell scope:- jdbc/WPSDB
- jdbc/BPEDB
- jdbc/mashupDS
- jdbc/CommonDB
- jdbc/PerformanceDB
- jdbc/TeamWorksDB
- jdbc/ECMDB
- jdbc/ECMDBXA
- jdbc/SharedDb
Minimum connections The minimum number of physical connections to maintain. Until this number is exceeded, the pool maintenance thread does not discard physical connections. Statement cache size The number of statements that can be cached per connection. This parameter is under Resources > JDBC > Data sources > WebSphere Application Server data source properties. - To check the JVM tuning parameters for the
deployment manager, click System Administration > Deployment Manager. Under Server
Infrastructure, click Java and
Process Management > Process definition > Java Virtual Machine.
Table 3. JVM tuning parameters Parameter Definition Comments Scope Initial heap size The initial heap size available to the JVM code, in megabytes. For multiple source nodes, if the value is the same across all nodes, it is migrated to the target. If the values are different, the maximum value is used for all nodes in the target environment. No scope limitations. Maximum heap size The maximum heap size available to the JVM code, in megabytes. For multiple source nodes, the maximum value is applied to the target environment. For example, if there are two source nodes in the source environment, the heap size values are retrieved from both the source node agents and the larger of the heap size values (if they are different) is applied to all target node agents. Verbose garbage collection Whether to use verbose debug output for garbage collection. The default is not to enable verbose garbage collection. For multiple source nodes, if the value is the same across all nodes, it is migrated to the target. If the values are different, the default value (disabled) is used for all nodes in the target environment. Disable web service address caching Disables address caching for web services. This is a JVM custom property. It is not required. For multiple source nodes, if the value is the same across all nodes, it is migrated to the target. If the values are different, this property is not migrated. - To check the thread pool tuning parameters,
click Servers > Server
Types > WebSphere application servers and click the server name. Under Additional
properties, click Thread pools.
Click the thread pool.
Table 4. Thread pool tuning parameters Parameter Definition Comments Scope Maximum connections The maximum number of physical connections that can be created in this pool. For multiple source nodes, the maximum value is applied to the target environment. These properties are migrated for each cluster member. They are migrated for the following thread pools: - default
- WebContainer
- ORB.thread.pool
- SIBFAPInboundThreadPool
- SIBFAPThreadPool
- SIBJMSRAThreadPool
Minimum connections The minimum number of physical connections to maintain. For multiple source nodes, if the value is not the same across all nodes, it is not migrated to the target. The default target value is used. - To check the JMS topic connection factory
tuning parameters, click Resources > JMS > Topic connection factories. Click the connection factory and click Connection
pool properties. The values of the following performance tuning properties are also migrated automatically. If you have multiple nodes in the source environment, in most cases, the value is the same across all nodes. If the values are different, the maximum value is used for all nodes in the target environment.
Table 5. Topic connection factory tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Maximum connections The maximum number of connections. These properties are migrated only in the application cluster scope. They are migrated for the following topic connection factories: - TWClientConnectionFactory
- cacheMessageConnectionFactory
Minimum connections The minimum number of connections to maintain. - To check the transaction service tuning parameters,
click Servers > Server
Types > WebSphere application servers and click the server name. Under Container
services, click Transaction Service.
Table 6. Transaction service tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Total transaction lifetime timeout The default maximum time, in seconds, allowed for a transaction that is started on this server before the transaction service initiates timeout completion. Any transaction that does not begin completion processing before this timeout occurs is rolled back. If you set this value to 0, the timeout does not apply and the value of the maximum transaction timeout is used instead.
These properties are migrated in the deployment manager and cluster member scope. Client inactivity timeout The maximum duration, in seconds, between transactional requests from a remote client. Any period of client inactivity that exceeds this timeout results in the transaction being rolled back in this application server. If you set this value to 0, there is no timeout limit.
- To check the web container tuning parameters,
click Servers > Server
Types > WebSphere application servers and click the server name. Under Web Container
Settings, click Web container > Session management.
Table 7. Web container tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Enable cookies Whether session tracking uses cookies to carry session IDs. If cookies are enabled, session tracking recognizes session IDs that arrive as cookies and tries to use cookies for sending session IDs. If cookies are not enabled and URL rewriting is enabled, session tracking uses URL rewriting instead of cookies. The default value is true.
These properties are migrated for each cluster member. Restrict cookies to HTTPS sessions Whether session tracking uses secure cookies that can only be sent back over an encrypted HTTP connection (HTTPS). When this feature is enabled, session cookies over an HTTP connection no longer work. The default value is false.
To find this parameter, under Web Container Settings, click Web container > Session management > Cookies.
- To check the work manager information tuning
parameters, click Resources > Asynchronous beans > Work managers. Click the work manager.
Table 8. Work manager information tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Maximum number of threads The maximum number of threads to be created in the thread pool. The maximum number of threads can be exceeded temporarily when Growable is selected. These additional threads are discarded when the work on the thread completes. These properties are migrated only in the application cluster scope. They are migrated for the following work managers: - BPENavigationWorkManager
- DefaultWorkManager
Minimum number of threads The number of threads to be kept in the thread pool, created as needed. Work request queue size The size of the buffer that the thread pool of the work manager uses to pull requests from. Note: The bpm-em-workmanager is migrated automatically during the migration of the 100Custom.xml file.
- If you are migrating from a network deployment
environment, the values of the following parameters are migrated automatically.
See the reference topic for more information.
Restriction: If you are migrating from a stand-alone environment, you must migrate these values manually.
- To check the single sign-on (SSO) configuration
properties, in the administrative console, click Security > Global security. Under Web and SIP security, click Single
sign-on (SSO).
Table 9. Single sign-on (SSO) configuration properties Parameter Definition Scope Enabled Whether to enable the single sign-on function. The default is true. All these properties are migrated. Domain name The domain name (for example, .ibm.com) for all single sign-on hosts. Requires SSL Whether the single sign-on function is enabled only when requests are made over HTTPS Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections. The default is false. Interoperability mode Whether to send an interoperable cookie to the browser to support back-level servers. The default is false. Set security cookies to HTTPOnly to help prevent cross-site scripting attacks Whether to add the HttpOnly browser attribute to cookies. This attribute prevents client-side applications (such as Java scripts) from accessing cookies to prevent some cross-site scripting vulnerabilities. The attribute specifies that LTPA and WASReqURL cookies include the HTTPOnly field. The default is true. Web inbound security attribute propagation Whether to propagate security attributes to front-end application servers. When this option is disabled, the single sign-on (SSO) token is used to log in and recreate the Subject from the user registry. The default is true. LTPA V2 cookie name The single sign-on (SSO) cookie name when using LTPA token version 2. The value must be different from the value of LTPA V1 cookie name (if present).
This property is migrated if it is present in the source environment. LTPA V1 cookie name The single sign-on (SSO) cookie name when using LTPA token version 1. This property is only available when interoperability mode is enabled. The default value is LtpaToken. The value must be different from the value of LTPA V2 cookie name (if present). This property is migrated if it is present in the source environment. - To check the log and trace tuning parameters,
click Troubleshooting > Logs
and Trace and click the scope. Click Diagnostic
Trace or IBM Service Logs.
Table 10. Log and trace tuning parameters Parameter Definition Scope Trace output Whether to log the diagnostic tracing data. These properties are migrated for each deployment manager server, node agent server, and cluster member. Enable service log Whether to enable the IBM service log, also known as the activity log.
- To check the single sign-on (SSO) configuration
properties, in the administrative console, click Security > Global security. Under Web and SIP security, click Single
sign-on (SSO).
- Completing configuration for IBM Business Process Manager
After migration, you must check and possibly change some configuration settings. - Completing configuration for Business Space
If you customized the Business Space component in the source environment, you must perform some additional tasks for the Business Space component after you migrate to IBM Business Process Manager V8.5.6, before you start your clusters and use Process Portal.
Previous topic: Starting the target environment
Next topic: Restarting and verifying the migration
Related information: