An advanced integration service is used to call a service
implemented in IBM® Integration
Designer from
a business process definition (BPD) (via a system task) or another
service (via a nested service).
Before you begin
An advanced integration service is a collaboration between
a business user working with IBM Process
Designer and
an integration developer working with IBM Integration
Designer.
For
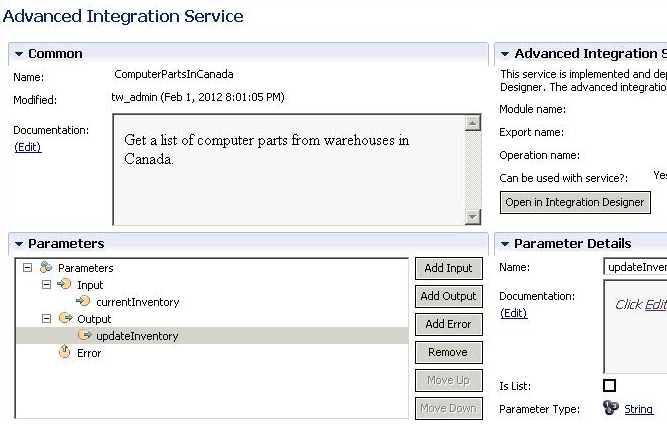
example, your business process may need a list of computer parts in
your warehouses in Canada. Checking with an integration developer,
you realize that a service is being built in
Integration Designer to query
the Canadian warehouses and return an inventory list of the computer
parts available. You could create an advanced integration service
that would use this
Integration Designer service
as an activity in your business process.
Note: Advanced integration
services are available only with IBM Business
Process Manager Advanced.
As suggested in Best practices when using IBM Integration Designer and IBM Process Designer
together, collaborate before defining your advanced integration service. For example, since
you may want to share this and other advanced integration services with many business processes, you
might select a toolkit to contain all your advanced integration services.
Note: Advanced integration services that are contained in a toolkit have a limitation that they can
be used only by BPDs in a process application.
To perform this task, you must be in the IBM Process
Designer desktop
editor.
To create services, you must have
access to a process application or toolkit in the Process Center repository.
Access to process applications and toolkits is controlled by users
who have administrative rights to the repository. For more information,
see Managing access to the Process Center repository.
About this task
To build an advanced integration service, follow these
steps.
Procedure
- Open the Process Designer desktop editor.
- Open a process application in the Designer view.
- In New Service,
enter a name for the service and click Finish. IBM Process
Designer displays
the diagram of the service with the default Start Event and End Event
components.
- Optional: In the Documentation field,
add a description for your service.
- In the Parameters section, add input,
output, and error parameters.
An input parameter defines
the name and type of data your business process sends to the service
in Integration Designer.
An
output parameter defines the name and type of data your business process
receives from the service in Integration Designer.
An
error parameter identifies an error or fault that might be thrown
by the service designed in Integration Designer. If you
want to catch a specific error using an error event in your process
model, enter an error name that matches the error code in the catching
error event.
Add a description for the parameter in the Documentation field.
Selecting Is List means the parameter is an
array (contains a set of data). In the Parameter Type field,
set the data type for the parameter.
- The Advanced Integration Service section
contains fields used in Integration Designer that will
be initially empty with the exception of Can be used with service?
The fields will be filled in when the service is implemented in Integration Designer. Can be
used with service? can also be changed at that time depending on the
implementation in Integration Designer.
- Module name: The name of the module in Integration Designer containing
the service implementation.
- Export name: The name of the export of
the module that exposes the service implementation. An export is the
endpoint to be used when invoking the service.
- Operation name: The name of the operation
of the service to be invoked.
- Can be used with service?: Not all implementations
of advanced integration services can be used with a service. If the
implementation cannot be used with a service, this field will be set
to No.
An advanced integration service can always be used by a Business
Process Definition whether the Can be used as service field is set
to Yes or No. It can also be used by the following services if the
field is set to Yes: a general system service, a human service or
an integration service. Do not use an advanced integration service
with these services if you see a No in this field or these services
will experience unexpected behavior.
The Yes or No value itself
is determined by the preferred interaction style and operation type
used by the associated export in
Integration Designer.
- Asynchronous style with a one-way operation type: Yes.
- Asynchronous style with a request-response operation type: No.
- Synchronous style with a one-way operation type: Yes.
- Synchronous style with a request-response operation type: Yes.
- An Open in Integration Designer button
lets you see the implementation created in Integration Designer. It can
only be used if Integration Designer is available.
- Save your work. From the menu, select
Results
An advanced integration service can be used as implementation
of a user task or a system task. If used by a user task, it is assigned
as specified via the assignments of the user task. If used by a system
task, it is run by the system user.
An advanced integration
service can also be emulated. In emulation, it behaves in the following
way:
- If used by a user task, it is assigned as specified via the Assignments
of the user task.
- If used by a system task then it will use the All users group.
When All users is shown in emulation, any user selected
will require authentication. Select the user you are currently authenticated
as and enter your credentials.
As discussed earlier, your service
is a collaborative arrangement. Should you move your advanced integration
service to another toolkit, notify the integration developer who implemented
your service. Your service and its implementation by Integration Designer are decoupled,
which means that even though you may move a service in Process Designer there
will not be an automatic corresponding movement in the implementation
by Integration Designer.
The
integration developer should use the refresh function to identify
the implementation that he needs to move and recouple with the advanced
integration service you moved in Process Designer.
What to do next
Use the information in
Authoring
services in IBM Integration Designer to continue developing
your advanced integration service. You can add services, service-related
functions, BPEL processes. monitor models, and more.