

Case management concepts
Case management applications consist of case types, document types, human services, and other components. A case management application is an application that case workers use to process cases.
Case management functions are only available if you have IBM BPM Advanced with the Basic Case Management feature installed.
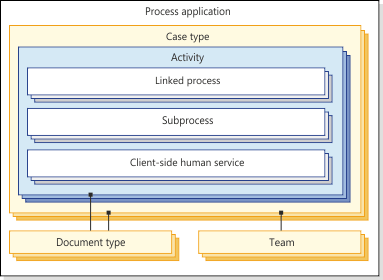
- Process application
- A process application contains one or more related case types that provide the documents, data, business processing, and routing to the case workers. For example, a process application for a human resources department might include a case type for new hires. The process application might also include a case type for retirement and a case type for employee termination.
- Case types
- Case types define the activities and might use document types to support the activity. Case types also specify the teams that must complete the activities to solve a business problem. The case type also includes properties that are shown to case workers in Process Portal. Case types make up a case management application. A case is an instance of a case type.
- Document types
- Document types help you to organize and classify the documents that belong to a case. You can provide more information about the documents by assigning properties to the document type. For example, a document type might be a job application form.
- Preconditions
- A case type can contain preconditions. A precondition determines the action to take if particular conditions are met in a case. You can use preconditions to determine process routing.
- Coaches
- You can define a launch user interface or an instance user interface for a business user to work with your case. The implementation of these user interfaces by a client-side human service can contain coaches. Human services with coaches can also be used to implement activities.
- Activities
- A case contains activities. An activity in a case is a discrete task that can be completed by a person or a system as part of that case. You can implement an activity as a user task, which is a client-side human service, a subprocess, or a linked process. For example, an activity might be to review new hire applications. A case is not complete until all activities that are marked as required during design are completed. Also, all activities that are started must be completed. For details about the states that an activity can be in, see Runtime states for activities in process applications.
- Linked process
- A case can call a reusable process, which is known as a linked process. Since a linked process is reusable, it can be used by many cases. For example, creating a customer account might follow a common set of steps; so, if created with a linked process, it might be used by many cases.
- Subprocess
- A subprocess is an option for encapsulating logically related steps within a case. Steps in a subprocess can directly access variables from the case. No data mapping is required. However, unlike a linked process, a subprocess can be accessed and instantiated only from the case that is using it. It is not reusable by any other case.
- Client-side human services
- Human services are the human actions in a process that must be completed for an activity. For example, a human service might be to review a job application form. There are two types of human services in IBM BPM; heritage human services, and client-side human services. Case activities use client-side human services. Use the Client-side human service editor to create and edit human services.
- Teams
- A team represents a specific business function. For example, a team might be an Applicant or Supervisor. You assign users and groups to teams. You can assign them at design time with the Designer or at run time with the Process Admin Console. Teams are associated with cases. You can also specify which users can start a case.