UNIX, Linux, and Windows: Side-by-side migration to a later version
Before you begin
If you are using IBM WebSphere MQ Version 7.0.1, you must ensure that you are running IBM WebSphere MQ Version 7.0.1.6 before installing the latest version of the product on the same server. Go to Fix Central to obtain the fix pack.
This scenario is one of three, which describe alternative ways to upgrade queue managers from an earlier version of the product. The other scenarios are as follows:
- Replace the earlier version with the latest version; see UNIX, Linux, and Windows: Single-stage migration to a later version.
- Run the latest version of the product alongside an earlier version ; see UNIX, Linux, and Windows: Multi-stage migration to a later version.
Read these three tasks to plan how you are going to migrate to the multi-installation environment of the latest version. The step-by-step migration scenario sits half-way between the single-stage and multi-stage migration scenarios.
These topics are for planning multi-installation migration. The planning topics guide you in deciding what other tasks you must perform to migrate queue managers and applications to the latest version. For the precise sequence of commands to upgrade a queue manager to the latest version, do the migration task for the platform you are interested in. All the tasks are listed by platform in the links at the end of this topic. As part of the queue manager migration task, back up your existing queue manager data. Even on a multi-installation server, queue managers cannot be restored to a previous command level after migration.
About this task
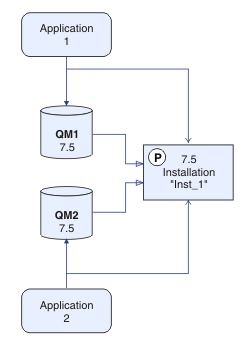
In the side-by-side
migration scenario, you install
the latest version of IBM WebSphere MQ alongside queue managers that continue to be associated with Version 7.0.1, or later.
- Stop all the queue managers.
- Uninstall the earlier version of the product.
- Migrate all the queue managers and applications to the latest version.
The side-by-side migration scenario is less flexible than multi-stage migration, and might not seem to have any advantages over it. However, side-by-side migration does have advantages over the multi-stage and single-stage approaches. With the side-by-side approach, because you uninstall the earlier version before starting any queue managers, you can assign an installation on the latest version to be the primary installation.
In the multi-stage approach, you cannot set an installation of the latest version to be the primary installation while you continue to run the earlier version.
Having the latest version installation as the primary installation has two benefits.
- With the latest version having the primary installation, many applications restart without reconfiguring their environment.
- IBM WebSphere MQ commands run against the primary installation, work without providing a local search path.
The advantage the side-by-side scenario has over the single-stage scenario is that you can install and verify the installation of the latest version of the product on the server before switching over to it.
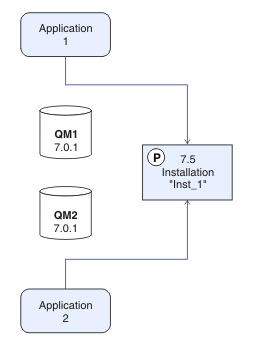
The description of the migration scenario starts with the example in Figure 1.
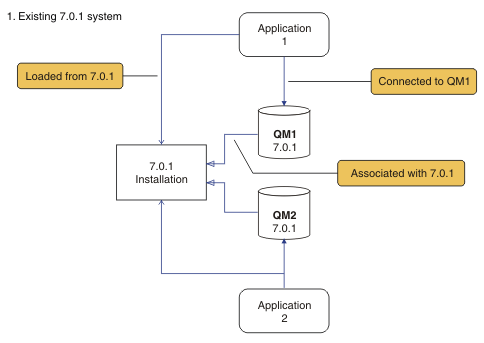
Four types of object are important to consider during migration: installations, queue managers, administrative procedures, and applications. The diagram shows the installation an application loads IBM WebSphere MQ libraries from, connections between applications and queue managers, and associations between queue managers and installations. Administrative procedures are omitted from the diagram. Administrative procedures contain IBM WebSphere MQ commands, and scripts that use commands.
Loading from 7.0.1
in Figure 1, refers to the IBM WebSphere MQ installation
from which the application loads the IBM WebSphere MQ library it requires;
see Loading IBM WebSphere MQ libraries. The connection
is a call to MQCONN or MQCONNX,
and has not changed from the earlier version of the product to the
latest version. The association is the installation that the queue
manager is associated with. The association is created either by running
the setmqm command, or by starting a queue manager
on the earlier version; see Associating
a queue manager with an installation.
To run a command, the operating system must find the command in a IBM WebSphere MQ installation. For some commands, you must run the command from the installation that is associated with the correct queue manager. IBM WebSphere MQ does not switch commands to the correct installation. For other commands, such as setmqinst, you can run the command from any installation that has the latest version of the product installed.
If an earlier version of the product is installed, the command that is run is the command for that version, unless the search path is overridden by a local setting. You can override the search path by running setmqenv. If Version 7.0.1 is not installed, you must set the correct path to run a command. If you have set a primary installation, the command that is run is the copy in the primary installation, unless you override the selection with a local search path.
Procedure
What to do next
You cannot reinstall an earlier version of the product on a system that has the latest, or any other, version of IBM WebSphere MQ installed.
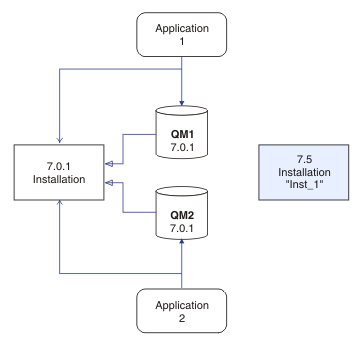
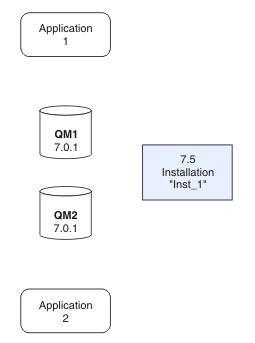
 If you have multiple
installations, note that queue managers that were configured to start
automatically, and remain after uninstalling
If you have multiple
installations, note that queue managers that were configured to start
automatically, and remain after uninstalling