Configuring a queue manager cluster
Use the links in this topic to find out how clusters work, how to design a cluster configuration, and to get an example of how to set up a simple cluster.
Before you begin
When you are designing your queue manager cluster you have to make some decisions. You must first decide which queue managers in the cluster are to hold the full repositories of cluster information. Any queue manager you create can work in a cluster. You can choose any number of queue managers for this purpose but the ideal number is two. For information about selecting queue managers to hold the full repositories, see How to choose cluster queue managers to hold full repositories.
Example
The smallest possible cluster contains only two queue managers. In this case both queue managers contain full repositories. You need only a few definitions to set up the cluster, and yet there is a high degree of autonomy at each queue manager.
DEMOCLSTR with
two queue managers called QM1 and QM2. 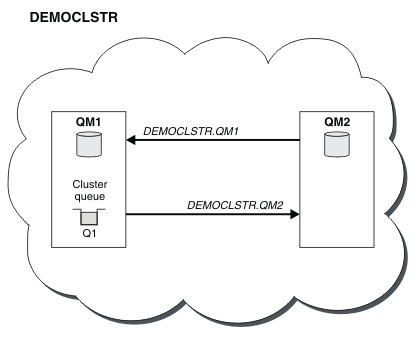
- The queue managers have long names such as
LONDONandNEWYORK. The same names are used in the advanced and workload balancing tasks. On IBM® WebSphere® MQ for z/OS®, queue-manager names are limited to four characters. - The names of the queue managers imply that each queue manager is on a separate machine. You could perform these tasks with all the queue managers on the same machine.
- The tasks use IBM WebSphere MQ script commands as they would be entered by the system administrator using MQSC commands. There are other ways of entering commands, including using the easier IBM WebSphere MQ Explorer. The point of using WebSphere MQ script commands is to demonstrate what IBM WebSphere MQ commands are used in the tasks.
For instructions on setting up a similar example cluster, see Setting up a new cluster.