Circular logging is the default behavior when a new database is created. (The logarchmeth1 and logarchmeth2 database configuration parameters are set to OFF.) With this type of logging, only full, offline backups of the database are allowed. The database must be offline (inaccessible to users) when a full backup is taken.
As the name suggests, circular logging uses a "ring" of online logs to provide recovery from transaction failures and system crashes. The logs are used and retained only to the point of ensuring the integrity of current transactions. Circular logging does not allow you to roll a database forward through transactions performed after the last full backup operation. All changes occurring since the last backup operation are lost. Since this type of restore operation recovers your data to the specific point in time at which a full backup was taken, it is called version recovery.
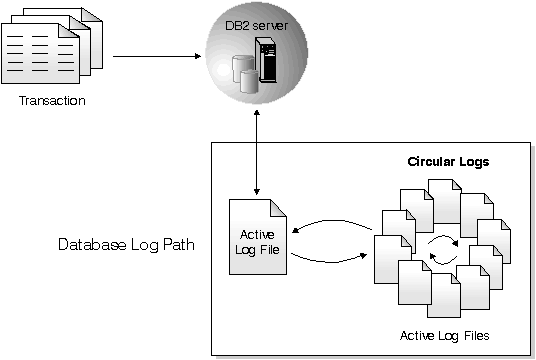
Active logs are used during crash recovery to prevent a failure (system power or application error) from leaving a database in an inconsistent state. Active logs are located in the database log path directory.