Various administrative authorities exist at the instance
level and at the database level. These administrative authorities
group together certain privileges and authorities so that you can
grant them to the users who are responsible for these tasks in your
database installation.
Instance level authorities
Instance level
authorities enable you to perform instance-wide functions, such as
creating and upgrading databases, managing table spaces, and monitoring
activity and performance on your instance. No instance-level authority
provides access to data in database tables. The following diagram
summarizes the abilities given by each of the instance level administrative
authorities:
- SYSADM -for users managing the instance as a whole
- SYSCTRL -for users administering a database manager instance
- SYSMAINT -for users maintaining databases within an instance
- SYSMON -for users monitoring the instance and its databases
A user with a higher-level authority also has the abilities
given by the lower level authorities. For example, a user with SYSCTRL
authority can perform the functions of users with SYSMAINT and SYSMON
authority as well.
Figure 1. Instance-level authorities
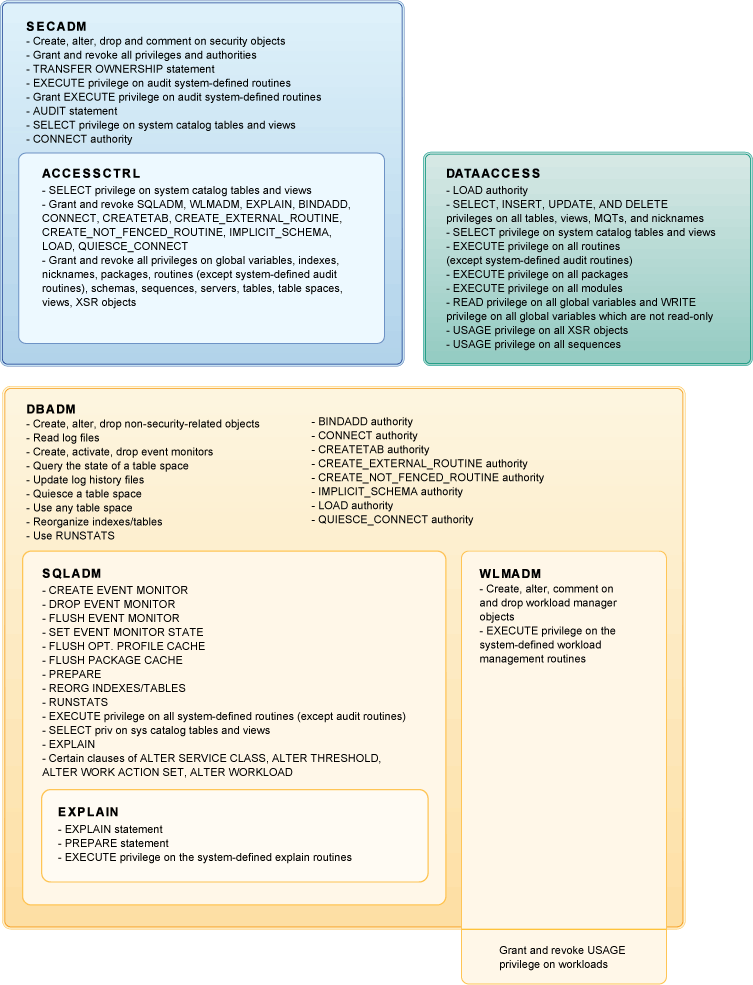
Database level authorities
Database level
authorities enable you to perform functions within a specific database,
such as granting and revoking privileges, inserting, selecting, deleting
and updating data, and managing workloads. The following diagram
summarizes the abilities given by each of the database level authorities.
The administrative database authorities are:
- SECADM - for users managing security within a database
- DBADM - for users administering a database
- ACCESSCTRL - for users who need to grant and revoke authorities
and privileges (except for SECADM, DBADM, ACCESSCTRL, and DATAACCESS
authority, SECADM authority is required to grant and revoke these
authorities)
- DATAACCESS - for users who need to access data
- SQLADM - for users who monitor and tune SQL queries
- WLMADM - for users who manage workloads
- EXPLAIN - for users who need to explain query plans (EXPLAIN authority
does not give access to the data itself)
The following diagram shows, where appropriate, which
higher level authorities include the abilities given by a lower level
authority. For example, a user with DBADM authority can perform the
functions of users with SQLADM and EXPLAIN authority, and all functions
except granting USAGE privilege on workloads, of users with WLMADM
authority.
Figure 2. Database-level authorities