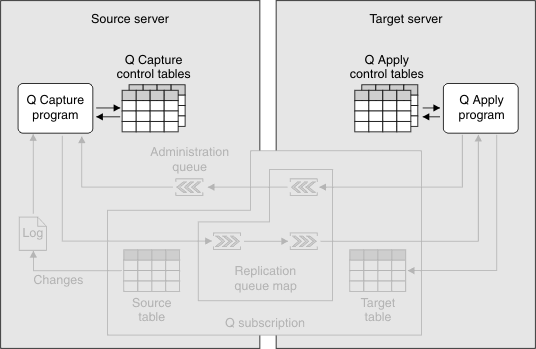
With Q Replication you replicate committed transactional data from source tables to target tables by using two programs: Q Capture and Q Apply.
The Q Capture and the Q Apply programs use a set of control tables to track the information that they require to do their tasks and to store information that they generate themselves, such as information that you can use to find out how well they are performing. You create these tables before you tell Q Replication what your replication sources and targets are.
The Q Capture program uses a set of control tables called Q Capture control tables. These tables contain information about your replication sources, the targets that correspond to them, and which WebSphere MQ queue manager and queues are being used by the Q Capture program. These tables also contain data that you can use to check and monitor the Q Capture program's performance, such as data about the Q Capture program's current position in the recovery log.
You can run multiple Q Capture programs. Each Q Capture program uses its own set of control tables. The schema that is associated with a set of Q Capture control tables identifies the Q Capture program that uses those control tables. This schema is called a Q Capture schema.
The Q Apply program uses a set of control tables called Q Apply control tables. These tables contain information about targets and where their corresponding sources are located, and information about which WebSphere MQ queue manager and queues are being used by the Q Apply program. Like the Q Capture control tables, these tables also contain data that you can use to check and monitor the Q Apply program's performance.
Like Q Capture programs, you can run multiple Q Apply programs. Each Q Apply program uses its own set of control tables. The schema associated with a set of Q Apply control tables identifies the Q Apply program that uses those control tables. This schema is called a Q Apply schema.
The following figure shows the infrastructure for a simple configuration in Q Replication.