Completing a Soft Stop of Sterling B2B Integrator from the System Troubleshooter
You can perform a soft stop from the system troubleshooter in the UI.
To complete a soft stop of Sterling B2B Integrator from the system troubleshooter:
- Log in to the system troubleshooter (Operations > System > Troubleshooter).
-
If running a cluster, select a node to shut down at the Select Node
field. If you need to shut down the container node along with the ASI node, you must first shut down
the container node and then the ASI node, because shutting down the ASI node first will disable the
soft stop UI for the container node.
In a clustered installation, you also can soft stop the container node by going to the Troubleshooter UI of the other live ASI node in the cluster and soft stopping the container node from there.
-
Click Soft Stop.
The soft stop page opens in a new popup window.
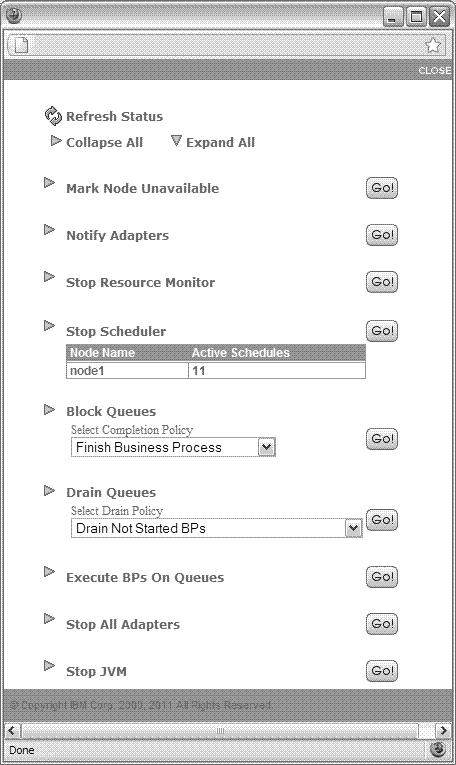
-
On the soft stop page, perform the following actions in the lettered sequence. When you run the
interactive soft stop process, it should continue until the JVM is stopped. You should not try to
undo any of the soft stop actions to bring back the system.
-
Mark Node Unavailable
In cluster installations, this is used to prevent business processes from coming from other nodes to the node that is marked unavailable.
-
Notify Adapters
This is used to notify all adapters that the server is shutting down so that adapters will stop taking new external requests.Note: This does not stop the adapters, which happens at the Stop All Adapters step later in this process.For the container node, you will see the adapter session status with two lists:
- A list of the business processes with a client adapter in session.
- A list of the running and queued business processes invoked by server adapters.
For the ASI node, the list of business processes with a client adapter session will show after you click the button Execute BPs On Queues. If a business process is a sub business process of the business process with a client adapter session, it will not inherit the client adapter session information from its parent, so it will not show up in the list. It is recommended that you use in-line invoking to invoke a sync BP.
The Transport Sessions section lists the business processes with active transport sessions. Those business processes are invoked by the adapters on the node that is being shut down. When the business process finishes, it will disappear from the list.

-
Stop Resource Monitor
This is used to stop the resource monitor.
-
Stop Scheduler
This is used to stop the scheduler in both clustered and standalone installations. In a clustered installation, this is used to move schedules to another live cluster node. A table lists the active schedules for the node.
-
Block Queues
This is used to stop the execution of business processes on a queue and not let nodes send any new business processes to it.
When you block a queue, if the business process completion policy is Finish Current Step, the executing business process will exit after it finishes the current step.
If the policy is Finish Current Execution Cycle, the executing business process will exit after it finishes the current execution cycle.
If the policy is Finish Business Process (the default value), the executing business process will not exit until it finishes.
Note: The Finish Current Step option does not stop a business process that is in the middle of an open communication session. Instead, the softstop waits until the session is terminated. Following termination, the business process will be marked HALTED_SOFTSTOP or move to another available node.For example, a business process starts a Sterling Connect:Direct® Begin Session service, and then a sleep service is active for 5 minutes. During that time, a softstop is triggered with the Finish Current Step completion policy. The BP will not be marked HALTED_SOFTSTOP or move to another node until the Sterling Connect:Direct End Session service is executed. This allows BP sessions to complete successfully without interruption.
-
Drain Queues
This is used to distribute the business processes in the queue to other live nodes (cluster installations only) or save them to the database for recovery (cluster and noncluster installations).
If the drain policy is Drain ALL BPs, then both started and unstarted business processes are distributed or saved. If it is Drain Not Started BPs (the default value), then just unstarted business processes are distributed or saved. If it is Drain No BPs, then no business processes are distributed or saved. If it is Drain Not Started BPs and No Open Session BPs, then the business processes that are unstarted and with no open server session are distributed or saved. Processes that are distributed to other queues use the same queue number.
Note: If the business process completion policy in the Block Queues step is Finish Business Process (the default value), then the specified drain policy will be honored. If the business process completion policy is Finish Current Step or Finish Current Execution Cycle, then the drain policy will be Drain ALL BPs.The following graphic shows an example of the results of selecting the Drain Not Started BPs option.
-
Execute BPs On Queues
This is used to allow the business processes on the queue to complete. The following graphic shows an example of this action.
- The BPs Execution Summary section shows the business process activity for all queues.
- In the BPs In Execution section, you can do the following:
- Click Show Service/Adapter Activity Status to show all service/adapter activity information. You can access the same information from the Administration UI by clicking Business Process > Monitor > Current Activities.
- Click Show business process Execution Thread Status to show all threads
executing business processes. You can access the same information from the Administration UI by
clicking Operations > Thread Monitor.
If there are business processes executing that you no longer want to wait for, they can be terminated via the Show business process Execution Thread Status link, using the Stop or Interrupt buttons.
- The BPs In Queue section gives detailed information about business process activity. If there are business processes remaining in the queue that you no longer want to wait for, they can be drained by clicking the Force Drain BPs link that appears in the BPs In Queue section when business processes are in the queue.
- The Client Sessions section lists business processes that have an open client session with adapters. You need to wait for those business processes to complete before you proceed to the next step to stop all adapters.

-
Stop All Adapters
This is used to shut down all adapters until you reach a timeout (in seconds) that is specified in the shutdown.timeout_for_adapters property in the noapp.properties_platform_ifcresources_ext.in property file. If the timeout value is zero, the adapters will not shut down gracefully.Note: You can also shut down adapters using the graceful adapter shutdown tool. For more information, see Graceful Adapter Shutdown.
-
Stop JVM
This is used to stop the Java™ Virtual Machine of a node in both clustered and standalone installations.Important: The soft stop only stops the noapp and ops JVMs. To stop the remaining Sterling B2B Integrator JVMs and stop the system processing, you must manually run a hard stop after the soft stop is complete.
-
Mark Node Unavailable