PCIe LP 8 Gb 2-Port Fibre Channel Adapter (FC 5273; CCIN 577D)
Learn about the specifications and operating system requirements for the feature code (FCs) 5273 adapter.
Overview
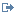
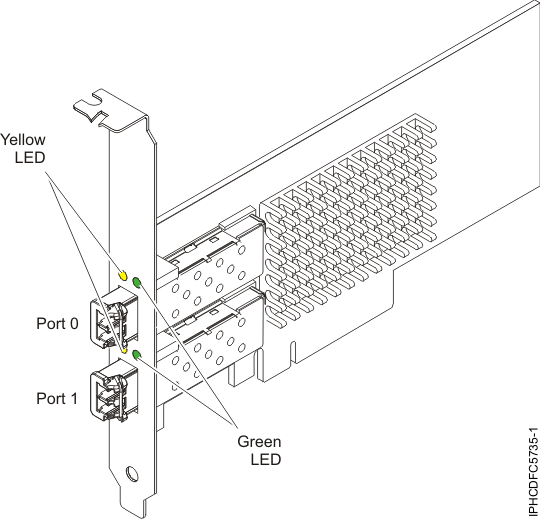
The PCIe LP 8 Gb 2-Port Fibre Channel Adapter is a high-performance adapter based on the Emulex LPe12002 PCIe Host Bus Adapter (HBA). The FCs 5273 is a full-height adapter. Each port provides single initiator capability over a fiber link. The ports have LC type connectors that use shortwave laser optics. The adapter connects to Fibre Channel switches and direct attached storage devices, operating at link speeds of 2, 4, and 8 Gbps. The adapter automatically negotiates with the switch to the highest speed that the switch is capable of. LEDs on each port provide information about the status and link speed of the port.
N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV) capability is supported through Virtual I/O Server (VIOS).
Adapter specifications
- Item
- Description
- FRU number
- 10N9824 (Designed to comply with RoHS requirement)
- Wrap plug FRU number
- 12R9314Note: The wrap plug is included with the card, and can also be purchased from IBM®.
- I/O bus architecture
- PCI Express (PCIe)
Base and Card Electromechanical (CEM) 2.0
x8 PCIe bus interface - Slot requirement
For details about slot priorities and placement rules, see PCIe adapter placement rules and slot priorities and select the system you are working on.
- Voltage
- 3.3 V
- Form factor
- Short, low-profile with standard-size bracket
- FC compatibility
- 2, 4, 8 Gigabit
- Cables
- Cables are the responsibility of the customer. Use multimode fiber optic cables with shortwave lasers that adhere to the following specifications:
- OM3: Multimode 50/125 micron fiber, 2000 MHz x km bandwidth
- OM2: Multimode 50/125 micron fiber, 500 MHz x km bandwidth
- OM1: Multimode 62.5/125 micron fiber, 200 MHz x km bandwidth
Table 1. Supported distances for multimode fiber optic cables Header Cable Type and Distance Rate OM1 OM2 OM3 2.125 Gbps 0.5 meters to 150 meters (1.64 feet to 492.12 feet) 0.5 meters to 300 meters (1.64 feet to 984.25 feet) 0.5 meters to 500 meters (1.64 feet to 1640.41 feet) 4.25 Gbps 0.5 meters to 70 meters (1.64 feet to 229.65 feet) 0.5 meters to 150 meters (1.64 feet to 492.12 feet) 0.5 meters to 380 meters (1.64 feet to 1246.71 feet) 8.5 Gbps 0.5 meters to 21 meters (1.64 feet to 68.89 feet) 0.5 meters to 50 meters (1.64 feet to 164.04 feet) 0.5 meters to 150 meters (1.64 feet to 492.12 feet) - Maximum number
- For details about the maximum number of adapters that are supported, see PCIe adapter placement rules and slot priorities and select the system you are working on.
Adapter LED
Green and yellow LEDs can be seen through openings in the mounting bracket of the adapter. Green indicates firmware operation and yellow signifies port activity. Table 2 summarizes the link rate conditions. There is a 1-second pause when the LED is off between each group of fast flashes (2, 3, or 4). Observe the LED sequence for several seconds to be sure that you have correctly identified the state.
| Green LED | Yellow LED | State |
|---|---|---|
| Slow flash | Off | Normal, link inactive or not started |
| On | 2 fast flashes | 2 Gbps link rate - normal, link active |
| On | 3 fast flashes | 4 Gbps link rate - normal, link active |
| On | 4 fast flashes | 8 Gbps link rate - normal, link active |
Power-on self test (POST) conditions and results are summarized in Table 3. These states can be used to identify abnormal states or problems. Follow the action to be taken for each condition.
| Green LED | Yellow LED | State | Action to be taken |
|---|---|---|---|
| Off | Off | Wake-up failure (dead board) | Perform AIX®, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| Off | On | POST failure (dead board) | Perform AIX, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| Off | Slow flash | Wake-up failure monitor | Perform AIX, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| Off | Fast flash | POST failure | Perform AIX, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| Off | Flashing | POST processing in progress | None |
| On | Off | Failure while functioning | Perform AIX, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| On | On | Failure while functioning | Perform AIX, IBM i, or Linux operating system diagnostics procedure. |
| Slow flash | Slow flash | Offline for download | None |
| Slow flash | Fast flash | Restricted offline mode, waiting for restart | None |
| Slow flash | Flashing | Restricted offline mode, test active | None |
| Fast flash | Off | Debug monitor in restricted mode | None |
| Fast flash | On | Not defined | None |
| Fast flash | Slow flash | Debug monitor in test fixture mode | None |
| Fast flash | Fast flash | Debug monitor in remote debug mode | None |
| Fast flash | Flashing | Not defined | None |
Operating system or partition requirements
If you are installing a new feature, ensure that you have the software that is required to support the new feature and that you determine whether any prerequisites must be met for this feature and attaching devices. To check for the prerequisites, see IBM Prerequisite website.
- AIX
- AIX 7.1, or later
- AIX Version 6.1, or later
- AIX Version 5.3, or later
- Linux
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Version 7, or later, with current maintenance updates available from Red Hat.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Version 6.1, or later
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11, Service Pack 1, or later, with current maintenance updates available from SUSE.
- Ubuntu 16.04.1, or later
- For support details, see the Linux Alert website.
- IBM i
- IBM i Version 7.2 or later
- IBM i Version 7.1, or later
Replacing Fibre Channel adapters by using hot swap
When hot swapping Fibre Channel adapters, be aware that device-related software for the storage devices might have extra devices (for example, the disk array router (dar) device that is associated with the fiber array storage technology (FAStT) or DS4800) that need to be removed. See the specific storage device documentation for information about how to remove these additional devices.
The new adapter has a unique worldwide port name (WWPN). Check the zoning and logical unit number (LUN) assignments to ensure that the new adapter functions as expected.