Troubleshooting
Problem
This document describes how Expert Cache works by minimizing the effect of synchronous DASD I/Os on a job.
Resolving The Problem
This document describes how Expert Cache works by minimizing the effect of synchronous DASD I/Os on a job.
How does expert cache work?
Expert Cache works by minimizing the effect of synchronous DASD I/Os on a job. The best candidates for performance improvement are those jobs that are most affected by synchronous DASD I/Os. Once started, Expert Cache monitors the Direct Access Storage Device (DASD) Input/Output (I/O) activity and logical reference pattern for each database file that is accessed within a shared storage pool. Then, it dynamically adjusts the size and type of I/Os for these files to maximize the use of main storage and minimize the number of DASD I/Os.
Reducing the number of DASD I/Os, particularly synchronous I/Os, can result in quicker processing. For interactive jobs, this generally means better response time. For batch jobs, it can mean completing your current batch work in less time or doing additional work within an existing batch window. In general, Expert Cache provides the best results under the following conditions:
How does expert cache work?
Expert Cache works by minimizing the effect of synchronous DASD I/Os on a job. The best candidates for performance improvement are those jobs that are most affected by synchronous DASD I/Os. Once started, Expert Cache monitors the Direct Access Storage Device (DASD) Input/Output (I/O) activity and logical reference pattern for each database file that is accessed within a shared storage pool. Then, it dynamically adjusts the size and type of I/Os for these files to maximize the use of main storage and minimize the number of DASD I/Os.
Reducing the number of DASD I/Os, particularly synchronous I/Os, can result in quicker processing. For interactive jobs, this generally means better response time. For batch jobs, it can mean completing your current batch work in less time or doing additional work within an existing batch window. In general, Expert Cache provides the best results under the following conditions:
| o | The main storage of the IBM System i products is not over-committed. Expert Cache cannot provide a performance benefit if the page-faulting rate of the shared pool is too high. |
| o | The CPU of the System i is not over-committed. Expert Cache cannot provide a performance benefit if a job is already constrained by the CPU. |
| o | DASD I/O is affecting job performance. Expert Cache attempts to improve the performance of your job by reducing DASD I/O contention. This is a difficult characteristic to measure on its own; however, the following indicators can help you determine if Expert Cache can help: -- Stand-alone batch jobs that cannot cause CPU use to reach 90%. -- A low ratio of logical to physical DASD I/Os. -- A high ratio of synchronous to asynchronous DASD I/Os coupled with DASD arm use in excess of 40% (highest single arm) |
| o | The data reference pattern of the job is sequential. Expert Cache can provide a significant benefit to jobs with a high percentage of DASD I/Os to sequential areas of data. It can also benefit jobs that do keyed reads from DASD as it brings in larger segments of the file index. The measurement of sequential I/Os requires the use of advanced tools which might require a great deal of time and expertise. The application designer should keep the database access method in mind when creating the programs. |
After meeting the above criteria, try using Expert Cache and measure the results with throughput and elapsed job time. You should not worry about CPU utilization or the number of I/Os (CPU utilization should be higher). Every job, configuration, and system is different. Try it and assess the results! Performance is particularly impressive in batch processing environments. The most important indicator is end user performance, whether that be elapsed run time for batch jobs, end-user response time, or interactive throughput.
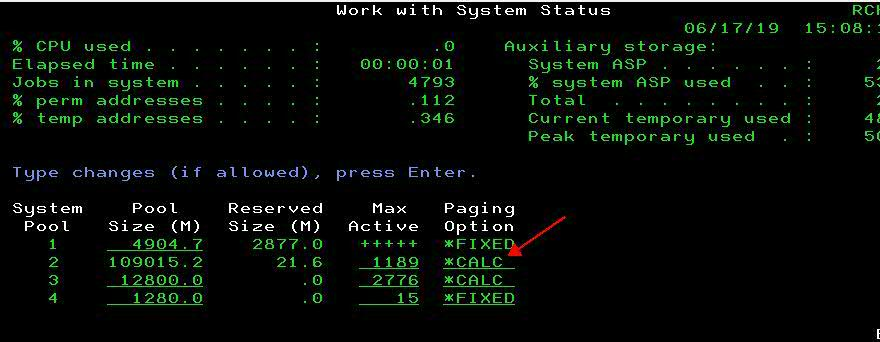
To enable Expert Cache change the Paging Option on the WRKSYSSTS screen to *CALC.

[{"Type":"MASTER","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB57","label":"Power"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU058","label":"IBM Infrastructure w\/TPS"},"Product":{"code":"SWG60","label":"IBM i"},"Platform":[{"code":"PF012","label":"IBM i"}],"Version":"6.1.0"}]
Historical Number
349093736
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
18 December 2019
UID
nas8N1015953